- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
AIIMS Doctors report Rare Case of Neurogenic Pulmonary Edema after High Voltage Electrical Shock
New Delhi: Electric shock injuries can be life-threatening as none of our organs is protected from it. It can lead to injuries like severe burns to fatal organ dysfunction such as cardiac arrest. A rare case of a 23 years old man who was presented with neurogenic pulmonary edema after being hit by a high voltage current, was reported by Dr. Ram Niwas, Dr Gopal Chawla, Dr Naveen Dutt, Dr Nishant Chauhan and Dr Vinod Sharma from All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), in the Indian Journal of Critical Care Medicine.
Read also: Patient felt electric shocks in legs -turned out a case of Vertebral Hydatidosis
There are a few cases that have reported pulmonary injuries due to electric shock. What makes this case special is that it is the first case which has reported neurogenic pulmonary edema (NPE) following an electric shock. Explaining the case to Medical dialogues Dr Ram Nivas, Assistant Professor, AIIMS, Jodhpur, and the corresponding author of the case wrote "This was a 23-year-old man, brought to emergency with an alleged history of electrical injury by high voltage current. He was not breathing but radial pulse was palpable. On examination, the patient had an entry wound in the right palm and exit wound in the left hand. ECG showed first-degree trio-ventricular block. Chest X-ray showed diffuse heterogeneous alveolar opacity suggestive of pulmonary edema. On performing screening echo biventricular function appeared normal with no pericardial effusion. USG of the chest showed multiple bilateral B lines with continuous pleura, with an initial lung ultrasound score 2 of 24. Blood gas analysis showed type 2 respiratory failure. The patient had normal electrolytes, CPK MB, NT‐pro BNP, renal and liver function test. "
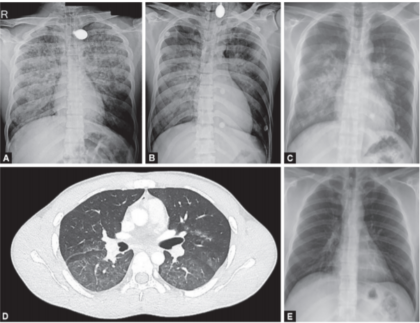
 (A) Initial chest X-ray showing pulmonary edema; (B) Chest X-ray after 24 hours; (C) Chest X-ray after extubation when patient is on NIV; (D) HRCT showing diffuse GGO; (E) Chest X-ray after 7 days showing complete resolution
(A) Initial chest X-ray showing pulmonary edema; (B) Chest X-ray after 24 hours; (C) Chest X-ray after extubation when patient is on NIV; (D) HRCT showing diffuse GGO; (E) Chest X-ray after 7 days showing complete resolutionHe further writes "Patient was intubated immediately and started on mechanical ventilation. Blood gas analyses showed severe hypoxemia (PaO2/FiO2 62.4). Non-contrast CT chest showed bilateral ground-glass opacities suggestive of pulmonary edema. Cardiac dysfunction was ruled out by normal cardiac enzymes and echocardiography. He was managed with high PEEP, low tidal volume with FiO2 of 100% initially and extubated on 3rd day. The patient was all right on follow up.
Read also: Is there a real life danger of electrocution with mobile phone charger?
"This case highlights that non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema may occur following electric injury and prompt diagnosis and management is crucial to decrease morbidity and mortality in such type of cases," concluded Dr Ram Niwas.
At our home, we use many electrical appliances such as extension cords or wall outlet, refrigerator, etc. While handling these electrical appliances, even the slightest carelessness can cost a life. Electrocution kills more than two thousand people every year in India. According to a survey conducted by the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), in 2015, more than 2,200 people lost their lives due to accidental fires that were caused by short circuits. This wasn't over yet, the following year saw over 11,000 electrical accidents in the country. Nearly 4,800 of these accidents were fatal. Accidents can happen all the time, due to various reasons—leaking water, unprofessional wiring, careless plugging of appliances or even the handy chord extensions.
For more details, please click on the link
Chawla G, Dutt N, R, Chauhan N, Sharma V. A Rare Case of Neurogenic Pulmonary Edema Following High-voltage Electrical Injury. Indian J Crit Care Med 2019; 23 (8):384-386. Available at: https://www.ijccm.org/doi/pdf/10.5005/jp-journals-10071-23226

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd