- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
A high fruit intake associated with less seborrheic dermatitis: Study
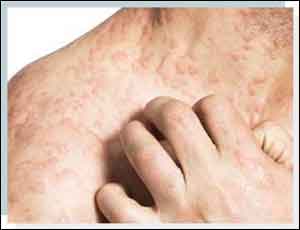
A high fruit intake was associated with less seborrheic dermatitis, whereas high adherence to a “Western” dietary pattern in females was associated with more seborrheic dermatitis, reports a new study published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
Seborrheic dermatitis appears on the body where there are a lot of oil-producing (sebaceous) glands like the upper back, nose and scalp. Its exact cause is unknown, although genes and hormones play a role. It most commonly affects adults between the ages of 30-60 and infants under 3 months.
Martijn G.H. Sanders and associates conducted to determine whether specific dietary patterns or total antioxidant capacity are associated with seborrheic dermatitis.
Participants in the Rotterdam Study with a skin examination and a food-frequency questionnaire were included. Total antioxidant capacity was assessed on the basis of the ferric reducing antioxidant potential of each food item. In total, 4,379 participants were included, of whom 636 (14.5%) had seborrheic dermatitis. In total, 4,379 participants were included, of whom 636 (14.5%) had seborrheic dermatitis.
Read Also: Short , repeated contact with nickel causes allergic contact dermatitis : Study
The study found that the “fruit” dietary pattern was associated with a 25% lower risk, while the “Western” dietary pattern was associated with a 47% increased risk in females. Other factors, such as the total antioxidant capacity, were not associated with it.
The authors suggested that the current treatments for the disease only provide a temporary relief, identifying modifiable lifestyle factors may reduce the disease burden.
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common skin condition that mainly affects the scalp. It causes scaly patches, red skin and stubborn dandruff. It can also affect oily areas of the body, such as the face, sides of the nose, eyebrows, ears, eyelids, and chest.
For reference log on to https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2018.07.027

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd