- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
Topical gel made from oral blood pressure drugs shown effective in healing chronic wounds
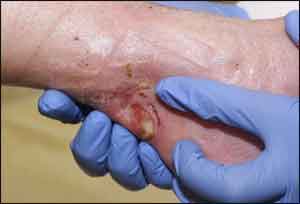
An international team of researchers led by Johns Hopkins has shown that a topical gel made from a class of common blood pressure pills that block inflammation pathways speeds the healing of chronic skin wounds in mice and pigs.
A report of the findings, published Oct. 16 in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology, marks efforts to seek approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to use the gel application in treatment-resistant skin wounds among diabetics and others, particularly older adults.
"The FDA has not issued any new drug approval for wound healing in the past 10 years," says Peter Abadir, M.D., associate professor of medicine at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and the paper's first author. "Using medicines that have been available for more than two decades, we think we have shown that this class of medicines holds great promise in effectively healing chronic wounds that are prevalent in diabetic and aged patients."
Chronic wounds, defined as skin injuries that fail to heal in a timely manner and increase the risk of infection and tissue breakdown, accounted for more than 100 million hospital visits in United States hospitals in 2008, according to Abadir.
In recent years, attention has turned to the skin's renin-angiotensin system (RAS), which is involved in the skin's inflammatory response, collagen deposition and signaling necessary for wound healing. Studies show that the RAS system is abnormally regulated in diabetic and older adults.
Abadir and colleagues experimented with gel formulations of angiotensin II receptor antagonists, or blockers, a long-standing class of drugs that includes losartan and valsartan, prescribed to treat hypertension. The drugs block RAS and increase wound blood flow, and the goal was to apply the gels directly to wounds, increasing wound tissue level of the drugs that promote faster healing.
Abadir and colleagues first tested 5 percent topical losartan on mice in three different phases of wound healing: group 1 treatment, for up to three days post-wound infliction to target the inflammatory phase; group 2 treatment, starting on day seven after wound infliction to target the proliferative/remodeling (later) phase of tissue healing; and group 3 treatment, starting the first day of wound infliction until closure to treat all wound healing phases. A fourth group was kept back as a control and given standard care and a placebo. Mice in group 2 experienced the most accelerated wound healing rate.
Next, Abadir and colleagues compared the effects of different concentrations of losartan and valsartan on young diabetic and aged mice during the proliferation/remodeling phase of wound healing, which involves the regrowth of normal tissue.
The results showed that valsartan was more effective in accelerating wound healing than losartan, without any significant difference in healing time between valsartan doses. Overall, 1 percent valsartan had the greatest impact on total closure compared with the other agents, and 10 percent losartan led to the worst wound healing, which Abadir says may be attributed to toxicity.
Final results showed that half of all mice that received 1 percent valsartan achieved complete wound healing, while only 10 percent of the mice given the placebo did.
Driven by 1 percent valsartan's promising results in mice, the researchers tested its effects on wounds among aged, diabetic pigs, as pig skin has more similar properties to the human skin.
Compared with pigs in the placebo group, wounds that received 1 percent valsartan healed much more quickly, and all 12 wounds were closed by day 50, compared with none of the placebo-treated wounds, the researchers say.
Of note, Abadir says, a low concentration (1 to 50 nanomoles) of valsartan was detected in the pigs' blood near the beginning of treatment, and none was detected later in the treatment course, suggesting that the drug acts locally on the tissues where it's absorbed, rather than affecting the entire body.
For comparison, oral ingestion of valsartan generally yields 4,000 to 5,000 nanomoles in the blood level for a human. This suggests that topical application of valsartan will not be absorbed into the bloodstream and could have unintended physiological effects, such as those that affected blood pressure, body weight or kidney function.
Finally, to determine the quality of 1 percent valsartan's biological effects on wound repair--not just rate of repair--Abadir and colleagues examined collagen content and tensile strength in the pigs' skin. Pigs treated with valsartan had a thicker epidermal layer (the outermost layer of the skin) and dermal collagen layer, as well as a more organized collagen fiber arrangement, all of which indicate 1 percent valsartan application leads to stronger healing skin, Abadir says.
"Our strategy for specifically targeting the biology that underlies chronic wounds in diabetics and older adults differs greatly from other approaches to wound care thus far. The topical gel likely enables a cascade of positive biological effects that facilitates and accelerates chronic wound healing," says Jeremy Walston, M.D., professor of medicine and the paper's senior author.
"Now that we've proven efficacy in animals, we're moving on to the next stage of FDA-required testing in humans. Hopefully, this medication will be available for public use in a few years, if further research bears out our results," adds Walston. Walston and colleagues envision that the medication could one day also be used to treat scars, wrinkles and other skin problems.
Twenty-nine million Americans have diabetes and 1.7 million are newly diagnosed each year. Of this group, approximately 900,000 will develop diabetic foot ulcers annually. With an aging population and incidence of diabetes increasing rapidly across the globe. Abadir estimates the total number of diabetic foot ulcers to be more than 20 million per year, with an estimated total cost of $25 billion annually in the U.S. alone.
For more details click on the link: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2017.09.030

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd