- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
New therapeutic target may reverse Diabetic retinopathy, finds a study
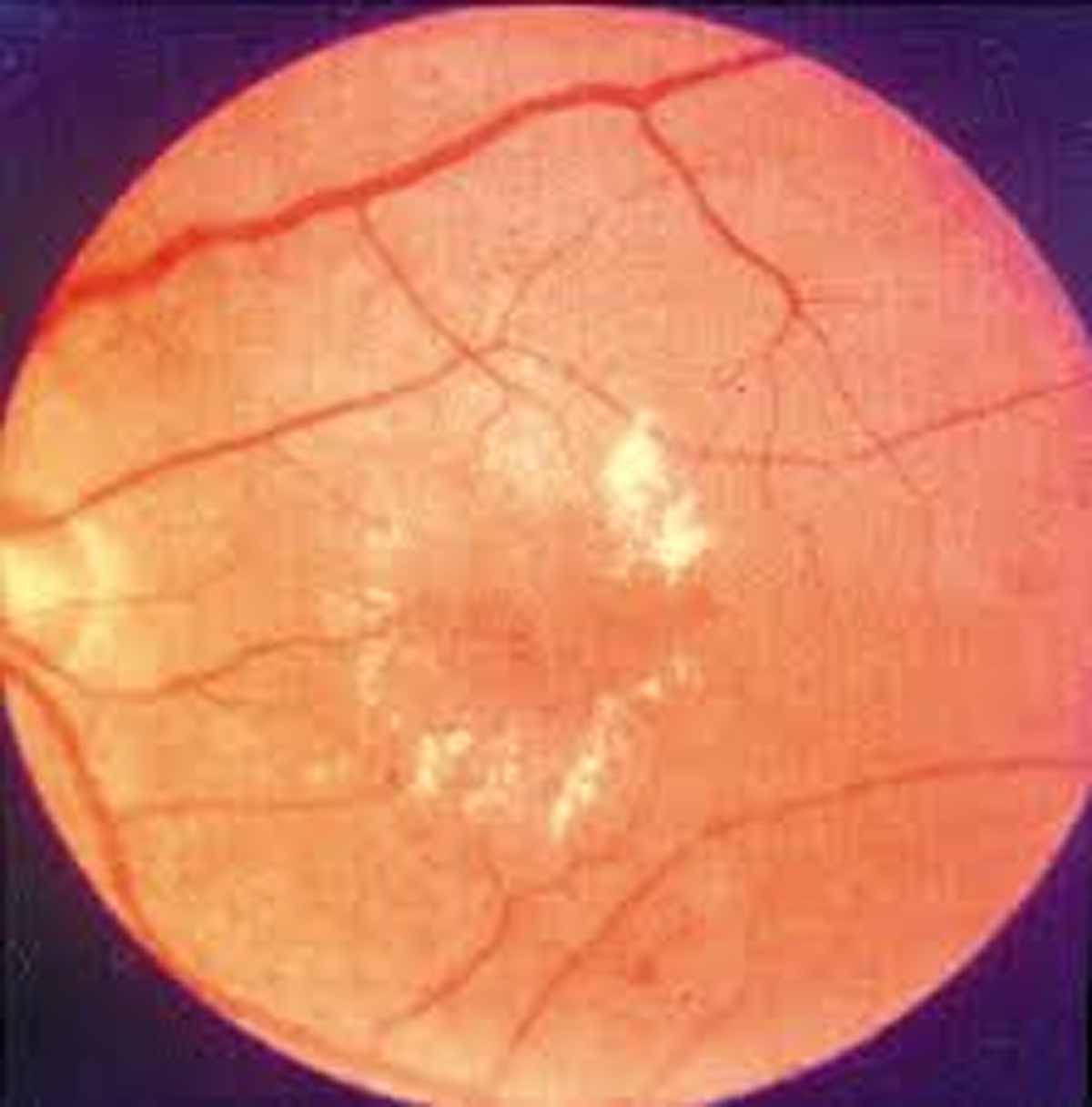
Philadelphia – Diabetic retinopathy is the most common microvascular disorder in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus patients. It not only damages the vision of patients but also has a considerable impact on the mental and social well being of the affected people. In a new study, scientists have found an enzymatic precursor called lysyl oxidase propeptide (LOX-PP) which may play a crucial role in promoting cell death in diabetic retinopathy. The findings were published in The American Journal of Pathology.
Unfortunately, till date, there is no cure for this debilitating ocular complication however, these findings published in the journal have provided a clue of a therapeutic target that may reverse this disorder.
‘We found that high blood sugar and diabetic conditions increased LOX-PP levels,” explained lead investigator Sayon Roy, Ph.D., of the Departments of Medicine and Ophthalmology at Boston University School of Medicine, Boston, MA, USA. “LOX-PP may induce cell death by compromising a cell survival pathway, and in retinas of diabetic rats, increased LOX-PP contributed to retinal vascular cell death associated with DR. Administration of recombinant LOX-PP alone was sufficient to induce cell death. This report shows novel functionality of LOX-PP in mediating cell death under high glucose condition in retinal endothelial cells as well as in diabetic animals.”
Studies in pancreatic and breast cancer cells suggest that LOX-PP overexpression may trigger cell death. The researchers, therefore, studied the role of LOX-PP in the retinal tissue. The retinal blood vessels of normal and diabetic rats and normal rats administered artificially synthesized LOX-PP (recombinant LOX-PP, rLOX-PP) directly into the eye, were examined. Changes associated with DR such as swelling, blood vessel leakage, blockage or thickening of vascular walls, and histologic indicators such as acellular capillaries (AC) and pericyte loss (PL) were studied.
More AC and PL were observed in the retinas of diabetic rats compared to controls. In non-diabetic rats, injection of rLOX-PP directly into the eye also increased the number of ACs and PLs compared to rats receiving a control injection.
The effect of high glucose on retinal endothelial cells grown in culture was also studied. Adding glucose to the cell cultures up-regulated LOX-PP expression and reduced AKT (protein kinase B) activation. Cells exposed to rLOX-PP alone exhibited increased cell death along with decreased AKT phosphorylation. The present study provides clear evidence that high blood sugar increases LOX-PP levels, which in turn promotes cell death. Furthermore, LOX-PP appears to induce cell death by compromising a pathway involved in cell survival.
“DR is the leading cause of blindness in the working-age population,” noted Dr. Roy. “Unfortunately, there is no cure for this devastating ocular complication. Our findings suggest a novel mechanism for high glucose-induced cell death involving LOX-PP, which may be a therapeutic target in preventing retinal vascular cell loss associated with DR.”
LOX is an extracellular enzyme responsible for cross-linking collagen and elastin molecules to form a stable extracellular matrix. The role of the LOX propeptide, LOX-PP, is less understood, although it may play a role in keeping LOX in an inactive state.
For more details click on the link:

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd