- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
Temporal subtraction images CT images improve detection of new brain infarcts on CT-Radio
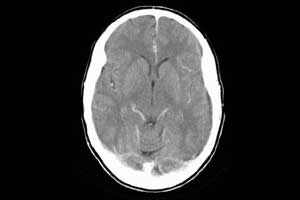
Temporal subtraction (TS) images of brain CT (computed tomography) significantly improves the detection of suspected brain infarction, finds a new study published in the journal European Radiology.
Thai Akasaka, Diagnostic Imaging, and Nuclear Medicine, Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto, Japan, and colleagues conducted the study to assess whether TS images of brain CT improve the detection of suspected brain infarction.
The study holds importance as although it is established that MRI is superior to CT in the detection of strokes, the first choice of modality for suspected stroke patients is often CT.
An observer performance study was conducted that involved the collection of forty-two sets of brain CT images of 41 patients, each consisting of a pair of brain CT images scanned at two-time points (previous and current) between January 2011 and November 2016. The 42 sets consisted of 23 cases with a total of 77 newly developed brain infarcts or hyperdense artery signs confirmed by two radiologists who referred to additional clinical information and 19 negative control cases.
Also Read: New blood test rules out the need for CT scans after traumatic brain injury
To create TS images, the previous images were registered to the current images by partly using a non-rigid registration algorithm and then subtracted. Fourteen radiologists independently interpreted the images to identify the lesions with and without TS images with an interval of over 4 weeks. A figure of merit (FOM) was calculated along with the jackknife alternative free-response receiver-operating characteristic analysis. Sensitivity, number of false positives per case (FPC) and reading time were analyzed by the Wilcoxon signed-rank test.
Key Findings:
- The mean FOM increased from 0.528 to 0.737 with TS images.
- The mean sensitivity and FPC improved from 26.5% and 0.243 to 56.0% and 0.153 (p < 0.0001 and p = 0.239), respectively.
- The mean reading time was 173 s without TS and 170 s with TS.
"Our findings show that the detectability of suspected brain infarctions was significantly improved with TS CT images." concluded the authors.
For more information log on to https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-018-5655-0

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd