- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
Now ‘Brain pacemaker ' to treat Epilepsy, Parkinson's
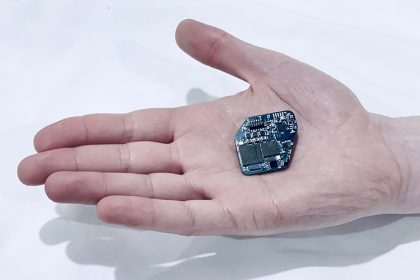
Engineers at UC Berkeley have developed a new neurostimulator that can listen to and stimulate electric current in the brain at the same time. This device can deliver fine-tuned treatments to patients with diseases like epilepsy and Parkinson’s.
Andy Zhou and Benjamin C. Johnson at UC Berkeley along with colleagues have developed a new device, named the WAND, that works like a “pacemaker for the brain,” monitoring the brain’s electrical activity and delivering electrical stimulation if it detects something amiss.
WAND, which stands for wireless artefact-free neuromodulation device, is both wireless and autonomous, meaning that once it learns to recognize the signs of tremor or seizure, it can adjust the stimulation parameters on its own to prevent the unwanted movements. And because it is closed-loop — meaning it can stimulate and record simultaneously — it can adjust these parameters in real-time.
These devices can be extremely effective at preventing debilitating tremors or seizures in patients with a variety of neurological conditions. But the electrical signatures that precede a seizure or tremor can be extremely subtle, and the frequency and strength of electrical stimulation required to prevent them is equally touchy. It can take years of small adjustments by doctors before the devices provide optimal treatment.
“The process of finding the right therapy for a patient is extremely costly and can take years. Significant reduction in both cost and duration can potentially lead to greatly improved outcomes and accessibility,” said Rikky Muller assistant professor of electrical engineering and computer sciences at Berkeley. “We want to enable the device to figure out what is the best way to stimulate for a given patient to give the best outcomes. And you can only do that by listening and recording the neural signatures.”
WAND can record electrical activity over 128 channels, or from 128 points in the brain, compared to eight channels in other closed-loop systems. To demonstrate the device, the team used WAND to recognize and delay specific arm movements in rhesus macaques. The device is described in a study that appeared in Nature Biomedical Engineering.

Simultaneously stimulating and recording electrical signals in the brain is much like trying to see small ripples in a pond while also splashing your feet — the electrical signals from the brain are overwhelmed by the large pulses of electricity delivered by the stimulation.
Currently, deep brain stimulators either stop recording while delivering the electrical stimulation, or record at a different part of the brain from where the stimulation is applied — essentially measuring the small ripples at a different point in the pond from the splashing.
“In order to deliver closed-loop stimulation-based therapies, which is a big goal for people treating Parkinson’s and epilepsy and a variety of neurological disorders, it is very important to both perform neural recordings and stimulation simultaneously, which currently no single commercial device does,” said former UC Berkeley postdoctoral associate Samantha Santacruz, who is now an assistant professor at the University of Texas in Austin.
Researchers at Cortera Neurotechnologies, Inc., led by Rikky Muller, designed the WAND custom integrated circuits that can record the full signal from both the subtle brain waves and the strong electrical pulses. This chip design allows WAND to subtract the signal from the electrical pulses, resulting in a clean signal from the brain waves.
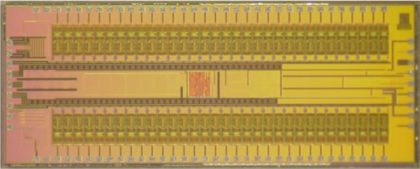
Existing devices are tuned to record signals only from the smaller brain waves and are overwhelmed by the large stimulation pulses, making this type of signal reconstruction impossible.
“Because we can actually stimulate and record in the same brain region, we know exactly what is happening when we are providing a therapy,” Muller said.
In collaboration with the lab of electrical engineering and computer science professor Jan Rabaey, the team built a platform device with wireless and closed-loop computational capabilities that can be programmed for use in a variety of research and clinical applications.
In experiments lead by Santacruz while a postdoc at UC Berkeley, and by and electrical engineering and computer science professor Jose Carmena, subjects were taught to use a joystick to move a cursor to a specific location. After a training period, the WAND device was capable of detecting the neural signatures that arose as the subjects prepared to perform the motion, and then deliver electrical stimulation that delayed the motion.
“While delaying reaction time is something that has been demonstrated before, this is, to our knowledge, the first time that it has been demonstrated in a closed-loop system based on a neurological recording only,” Muller said.
“In the future we aim to incorporate learning into our closed-loop platform to build intelligent devices that can figure out how to best treat you, and remove the doctor from having to constantly intervene in this process,” said Muller said.

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd