- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
Retinal changes may predict future heart disease
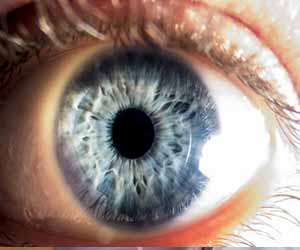
High blood pressure and arterial stiffness are two major risk markers for cardiovascular disease and incidentally they create easily detectable changes in retina that may predict a heart disease in future, according to new research.
"When blood pressure and arterial stiffness levels go up, this translates into a change in the small vessels at the back of the eye," said Alicja Rudnicka, a professor at the Population Health Research Institute, St. George's University of London, and lead author on the study. "These microvessels get narrower and more wiggly, or tortuous."
While these changes don't signal vision problems, Rudnicka said, "if what's happening in the rest of the body is reflected in what's happening at the back of the eye, what we see there could be a flag taking retinal morphology assessment from being just a research tool to incorporating it into clinical practice."
Previous studies have shown a relationship between the narrowing of retinal arteries and hypertension, along with a higher risk of cardiovascular events such as heart attacks, strokes or death. And some smaller studies have suggested a link between changes in retina vessels and higher blood pressure. But none have included such a large number of participants or used such a large number of consistently measured vessel segments, Rudnicka said.
She and her team analyzed images of retinal blood vessels for nearly 55,000 middle aged and older people in the UK Biobank data set, using a fully automated image analysis program that takes thousands of measurements of blood vessel diameter and tortuosity from digital retinal images. Using this system, they were able to examine 3.5 million blood vessel segments, she said.
The team is currently exploring whether what they measured 10 years ago predict which patients go on to develop heart disease.
"What we have now is one piece of the puzzle. It's a starter puzzle piece, and we need more to move forward," Rudnicka said. "If we can link the retinal vessel measurements of the past to what happens to these people years later, this will tell us whether these vessel changes came before cardiovascular disease and go on to predict those who go on to have a cardiovascular event."
Other studies have associated childhood obesity, high blood pressure and physical inactivity to abnormalities in eye vessels, suggesting that narrowing eye vessels are a biomarker for cardiovascular risk factors in children, said Dr. Henner Hanssen, lead author on a meta-analysis on this topic that included more than 18,000 children and adolescents.
"Microcirculation is a so-called window to the heart," said Hanssen, a professor of Preventive Sports Medicine and Systems Physiology at the University of Basel, Switzerland. "The vessels in the eye reflect what is going on in other organs, specifically the heart."
"The data that we have is very clear that at a very early age, in children 6 to 8 years old who are otherwise healthy, you can already see vascular alterations due to blood pressure levels that are on the high end of normal and only being overweight," he said.
"We don't know if this predicts worse outcomes when they become adults, but we have seen similar alterations in adults that are predictive of cardiovascular mortality and morbidity."
If Rudnicka's large, prospective study also confirms a link between retinal changes and heart disease and death, she said, it could provide health professionals with a quick, noninvasive alternative for determining a patient's CVD risk.
"This digital picture could potentially tell us very quickly," she said, "whether you are on the road to cardiovascular disease."
Dr Prem Aggarwal, (MD, DNB Medicine, DNB Cardiology) is a Cardiologist by profession and also the Co-founder of Medical Dialogues. He is the Chairman of Sanjeevan Hospital in Central Delhi and also serving as the member of Delhi Medical Council

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd