- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
People with depression at increased risk for SLE: JAMA
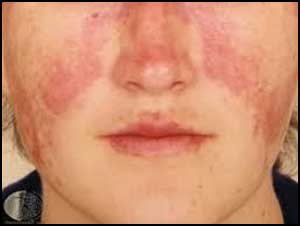
Boston, Massachusetts: Women with a history of depression are at more than double the risk of developing systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), suggests a new study published in the journal JAMA Psychiatry.
It has long been hypothesized that depression may increase the risk of developing autoimmune disease; however, the rigorous empirical evidence is sparse.
Andrea L. Roberts, Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, Massachusetts, and colleagues conducted the study to evaluate the association between depression and risk of incident SLE, a paradigmatic, systemic autoimmune disease.
Also Read: Vortioxetine- New antidepressant that improves sleep also
This 20-year prospective, longitudinal cohort study evaluated data collected from 2 cohorts of women participating in the Nurses’ Health Study (1996-2012) and the Nurses’ Health Study II (1993-2013). Data analyses were conducted from August 2017 to May 2018.
Incident SLE with 4 or more American College of Rheumatology criteria was ascertained by self-report and confirmed by medical record review. Depression was assessed repeatedly throughout follow-up according to whether women reported having received a clinician’s diagnosis of depression, regular antidepressant use, or a score of less than 60 on the 5-item Mental Health Inventory (MHI-5). Whether longitudinally assessed health risk factors (eg, cigarette smoking, body mass index, oral contraceptive use, menopause or postmenopausal hormone use, alcohol use, exercise, or diet) accounted for increased SLE risk among women with vs without depression was examined.
Data from 194 483 women (28-93 years of age; 93% white) were included.
Also Read: Adding Mirtazapine to SSRI as good as placebo in resistant depression: BMJ
Key Findings:
- Compared with women with no depression, women with a history of depression had a subsequent increased risk of SLE.
- Adjustment for body mass index, cigarette smoking, and oral contraception and postmenopausal hormone use slightly attenuated associations.
- The SLE risk was elevated with each of the 3 following depression indicators modeled separately: clinician’s diagnosis of depression, antidepressant use, and MHI-5 scores indicating a depressed mood.
- Associations remained strong when depression status was lagged by 4 years with respect to the outcome and when depression status at baseline was used as the exposure.
"Screening patients who have depression for a family history of autoimmune disease and considering the possibility that they may be developing an autoimmune disease would be helpful," said Dr. Roberts.
This study contributes to increasing evidence that depression may be associated with an increased risk of SLE and suggests that the association is not fully explained by measured health factors or behaviors.
For further reference log on to 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.2462

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd