- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
Oxysterols guide gut immune cells and are involved in inflammatory bowel disease
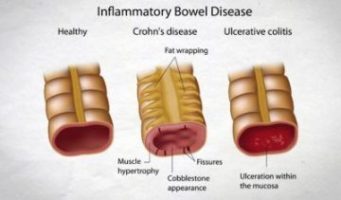
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden report that cholesterol metabolites cause specific immune cells in the large intestine to move, which lies behind the formation of the immune system's important lymphoid tissue in the intestine. The study, published in the journal Immunity, paves the way for a new possible treatment for patients with inflammatory bowel disease.
Inflammatory bowel disease is a common and severe disease that has no cure. Normally, the immune cells of the gut accumulate and communicate with each other in the lymphoid tissue. But, for those who have autoimmune inflammatory bowel disease, such as ulcerative colitis, the lymphoid tissue can react to the body's own cells and cause chronic inflammation.
Hitherto, it has not been known which signals control the formation of the lymphoid tissue in the large intestine. But, now scientists at Karolinska Institutet have discovered that cholesterol metabolites, called oxysterols, stimulate specific immune cells in the large intestine, called innate lymphoid cells (ILCs), to form lymphoid tissue in both health and in disease.
"We have discovered that ILCs use a surface protein called GPR183 to sense the oxysterols, which attracts ILCs to specific sites in the large intestine where lymphoid tissue is formed," says Tim Willinger, researcher at Karolinska Institutet's Department of Medicine in Huddinge, who has led the study.
"Our findings are relevant to humans because inflammatory lymphoid tissue contributes to tissue damage in inflammatory bowel disease. We have discovered that patients with ulcerative colitis have higher levels of oxysterol-producing enzymes than healthy controls. The results indicate that oxysterols and GPR183 are involved in ulcerative colitis," he says.
One way to treat inflammatory bowel disease could, therefore, be to attempt to inhibit GPR183 or oxysterol production.
"This treatment option is attractive, because GPR183 belongs to a group of molecules that are excellent targets for drug treatment," says Dr Willinger.

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd