- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
Effect of Obesity on Women's Health- Dr Rajeshwari Laxman Khyade
Obesity is an important public health crisis in the major parts of the world with increasing prevalence in many industrial nations. It is panning endemic and warrants urgent measures as it increases morbidity and mortality. It is also a socioeconomic burden to the family.
WHO CLASSIFICATION OF OBESITY BASED ON BODY MASS INDEX (BMI)
Grade 1:-Overweight -BMI 25- 29.9 KG/M2
Grade 2:-Overweight – BMI – 30 -39.9 KG/M2
Grade 3:- Overweight – BMI >= 40 KG/M2
CLASSIFICATION OF OBESITY BASED ON BODY FAT
MEN – Percentage of body fat greater than 25% with 21-25% being borderline
WOMEN – Percentage of body fat greater than 33% with 31- 33 % being borderline
EFFECT OF OBESITY ON ADOLESCENT GIRLS
The adolescent period is associated with a change in eating and active behavior in girls. Less resistance from parents and choice of food, along with decreased participation in physical activity and outdoor sport, increased time spent on screen time be it mobiles, laptops, and television decreases melatonin secretion due to staying up late in the night.

EFFECTS OF OBESITY ON ADOLESCENT GIRLS
- Early onset of menarche/body dymorphism/ short stature
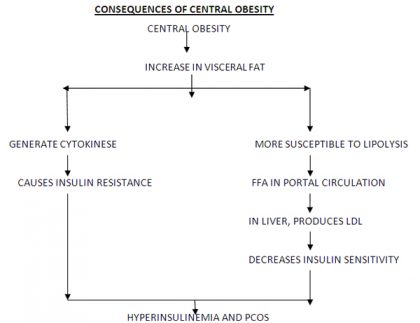
- Hyperinsulinemia
- PCOS
- Hirsutism, acne
- Obese adolescents have increased risk of developing the chronic disease later in life
- Acanthosis Nigricans
- Psychological disturbance, anxiety, depression due to body shaming.
EFFECT OF OBESITY ON REPRODUCTIVE WOMEN
There is a coexistence of obesity and PCOS. Therefore she may have
- Menstrual disturbance either oligo or anovulation leads to Infertility.
- Hyperandrogenism
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Dyslipidemia
EFFECT OF OBESITY ON WOMEN WITH PREGNANCY
Early abortions, Gestational Diabetes Mellitus, Hypertension, Big Baby, increased operative interference, increased chances of LSCS, Postoperative wound infection, prolonged hospital stay, increased financial burden on the family.
EFFECT OF OBESITY ON PREMENOPAUSAL WOMEN
- Dysfunctional uterine bleeding, polymenorrhea
- Increased risk of fibroid
- Adenomyosis
- Endometrial Hyperplasia
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Hypertension
- Hypothyroidism
EFFECT OF OBESITY ON POSTMENOPAUSAL WOMEN
- Increased risk of Endometrial Carcinoma
- Increased risk of Ovarian and Breast Cancer
- Increased risk of Gall Bladder stones and Carcinoma
- Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis
MEASURES TO CURB OBESITY
Maintaining an ideal body weight throughout different stages of one’s life is very important, not only to avoid risk but also to prevent the complications, hence of the methods to reduce obesity.
- Lifestyle modification – Healthy diet with more proteins, a moderate amount of complex carbohydrates and fats
- To avoid aerated drinks, juices, etc
- To eat fruits rather than juices
- Adoption of the Mediterranean diet which contains more vegetables and fruits, nuts and lean meats, eggs, etc
- Avoid fried and junk food
- Daily moderate exercises like cycling, brisk walking, swimming, aerobics and HIIT (High-Intensity Interval Training) at least for 150-250 minutes/week
- Indulging in outdoor sports like badminton, lawn tennis, especially for adolescent girls
- Regular health checkups for BMI, Lipid profiles, blood sugar levels.
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF OBESITY
INDICATIONS – BMI >= 30 KG/M2 WITHOUT CO-MORBIDITIES
BMI >= 27 KG/M2 WITH CO-MORBIDITIES
DRUGS USED IN THE MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF OBESITY
- Orlistat 120 mg oral 3 times/day with meals containing fat.
- Lorcaserin 10 mg orally twice daily.
- Phentermine plus Topiramate combination.
- Metformin for patients with diabetes mellitus.
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF OBESITY (BARIATRIC SURGERY)
INDICATIONS - BMI >=40 KG/M2 WITHOUT COMORBIDITIES
BMI >=35 KG/M2 WITH COMORBIDITIES (DM, HTN, DYSLIPIDEMIA)
SURGERIES – Open /Laparoscopic
1. Malabsorptive procedures
- Roux –en- Y Gastric Bypass
- Biliopancreatic diversion with or without duodenal switch
2. Restrictive Procedures
- Gastric Banding
- Vertical Banded Gastroplasty
- Sleeve Gastrectomy
3. Liposuction
Reduces Body Mass Index but not risk factors for Coronary Heart Disease / Type 2 DM
ADVANTAGES OF BARIATRIC SURGERY
- Reduces mortality
- Long term weight loss ( maintained up to 10 years )
- Reduction in co-morbidities such as DM, Hyperlipidemia, Hypertension and Obstructive Sleep Apnoea
- Improved fertility in women with maternal and neonatal complications.
DISADVANTAGES OF BARIATRIC SURGERY
The patient should be evaluated and followed by a multidisciplinary team for diet, physical activity,
behavioural and social support after bariatric surgery.
- Nutritional support.
- Regular assessment for anaemia, Vitamin B12 levels, 24 hours urinary calcium, Vitamin A levels with supplements along with micronutrients.
Nutritional supplementation with micronutrients, VitaminA, VitaminK, thiamine, selenium, zinc, copper.
Dr. Rajeshwari Laxman Khyade is a consultant obstetrician and gynecologist and infertility specialist at Saifee Hospital, Somaiya Superspeciality, and K.J.Somaiya Medical College.

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd