- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
No role of steroids in management of isolated acute urticaria, finds trial
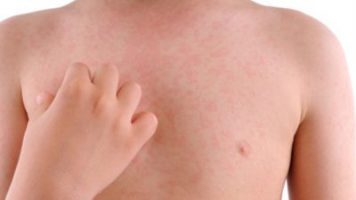
Despite standard use for the itching associated with urticaria (commonly known as hives), prednisone (a steroid) offered no additional relief to emergency patients suffering from hives than a placebo did, according to a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, parallel-group study published online yesterday in Annals of Emergency Medicine ("Levocetirizine and Prednisone Are Not Superior to Levocetirizine Alone for the Treatment of Acute Urticaria: A Randomized Double-Blind Clinical Trial").
"Prednisone is a strong and great drug for certain problems, but it is no better than antihistamine treatment for patients who are itching with hives," said lead study author Caroline Barniol, MD, of the Centre Hospitalier Universitaire in Toulouse, France. "The antihistamine levocetirizine alone achieved full itching relief within 2 days for 76 percent of patients. With the addition of prednisone, the relief scores were actually worse."
At 2-day follow-up, 62 percent of patients treated with levocetirizine (an antihistamine) and prednisone had an "itch score" of 0, while 76 percent of those in the placebo group (levocetirizine and placebo) had an itch score of 0. Thirty percent of patients in the prednisone group and 24 percent in the placebo group reported relapses.
Acute urticaria, or hives, is a fairly common presentation in the emergency department. Itching is frequently associated with hives and can interfere with daily activities and sleep. International guidelines published in 2013 stated that a short course of oral corticosteroids may be helpful to reduce disease duration for acute hives. Prednisone is commonly prescribed in the emergency department to treat them, along with antihistamines.
"Despite the evidence that second-generation H1-antihistamines treat acute urticaria without disturbing side effects, many physicians believe that corticosteroids are still the most effective treatment to obtain rapid symptom relief," said Dr. Barniol. "Our results do not support the addition of corticosteroid to antihistamines as a first-line treatment of uncomplicated acute hives. Even if short-term treatment with corticosteroids does not cause clinically significant toxicity, recurrent or long-term treatment may have deleterious effects."

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd