- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
Nitisinone protects against UV light and promotes normal vision in albinism
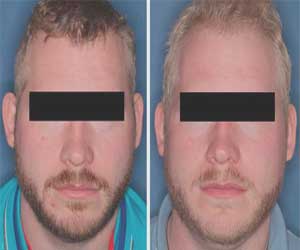
Drug nitisinone protects against UV light and promotes a normal vision by increasing melanin production in some people with oculocutaneous albinism.Oculocutaneous albinism type 1B (OCA-1B), a rare genetic disease that causes pale skin and hair and poor vision. Increased melanin could help protect people with the condition against the sun’s UV rays and promote the development of normal vision according to a small pilot clinical study at the National Eye Institute. The study results were published in JCI Insight.
Oculocutaneous albinism (OCA) is a rare inherited disease caused by mutations in genes needed to make melanin, a dark-colored pigment found in hair, skin, and eyes. In the United States, the most common form of OCA is OCA-1, which is caused by mutations in the gene that codes for the enzyme tyrosinase. Tyrosinase function — the breakdown of the amino acid tyrosine into its component parts — is critical for the production of melanin. People with OCA-1B, like those who participated in this study, have some tyrosinase, but it functions poorly. People with OCA-1A have no tyrosinase at all. Approximately one in 17,000 people worldwide have a form of OCA.
“Because the greatest vision problems for people with albinism occur during the early development of the eye, our eventual goal is to work with infants,” said Brian Brooks, M.D., Ph.D., clinical director at NEI and lead author of the study. “The purpose of this pilot study was to explore whether nitisinone is safe and whether we could pick up a signal that the drug works.”
A small pilot clinical study at the National Eye Institute (NEI) suggests that the drug nitisinone increases melanin production in some people with oculocutaneous albinism type 1B (OCA-1B), a rare genetic disease that causes pale skin and hair and poor vision.
The study followed three women and two men over 18 months, including 12 months on a daily oral 2 mg dose of nitisinone, and six additional months without the drug. While on nitisinone, most study participants showed a slight darkening of skin and hair. One participant’s skin darkened slightly after sun exposure. However, the researchers were unable to detect clinically significant changes in eye melanin or in visual acuity. With improvements in imaging of the iris, and with younger patients, Brooks and colleagues hope subtle changes in the eye will be more apparent.
Nitisinone increases the concentration of the amino acid tyrosine in the blood. In people with OCA-1B, Brooks believes that the higher levels of tyrosine help stabilize mutated tyrosinase and make the enzyme more effective. Brooks’ previous studies have shown that nitisinone has no effect in OCA-1A, where there’s no tyrosinase to stabilize, and OCA-3, where a different part of the melanin pathway is affected, so his team doesn’t intend to pursue this drug for patients with those forms of albinism. Nitisinone is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat a rare metabolic disease called tyrosinemia, which can cause liver and neurological problems.
“We’re evaluating OCA-2 and OCA-4 in mice, and we’re hopeful that this drug might have some effect,” said Brooks. In the meantime, he hopes to start a new, larger trial of nitisinone for teenagers with OCA-1B.
“Melanin is crucial for normal visual development during infancy, but the eye continues to develop and change throughout childhood and into the teenage years,” Brooks said. For this reason, Brooks thinks nitisinone might improve iris pigmentation and visual acuity in teens and could have a bigger effect in younger children with OCA-1B.
On February 28, NIH will recognize Rare Disease Day, established in 2008 to raise awareness about rare diseases and the unique challenges faced by patients and their families. In the United States, a disease is considered rare if it affects less than 200,000, or approximately one in 1700, people. About 80 percent of rare diseases are caused by inherited gene defects, and many of these, like OCA, lack effective treatments. NEI is committed to supporting basic and clinical research into rare diseases that affect vision.

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd