- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
New urine dipstick test to detect blinding disease- onchocerciasis
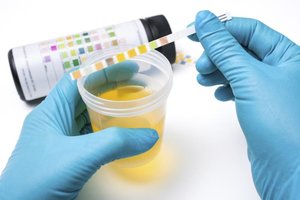
A urine diagnostic test for detection of river blindness (also called onchocerciasis) causing parasitic worms has been developed by the scientists at Scripps Research, according to a new study published in the journal ACS Infectious Diseases.
Onchocerciasis is a tropical disease that afflicts 18 to 120 million people worldwide and is the second leading cause of preventable blindness.
In this study, Kim D Janda, Ely R. Callaway Jr. Professor of Chemistry and member of the Skaggs Institute for Chemical Biology at Scripps Research and colleagues report the development and assessment of a NATOG (biomarker N-acetyl-tyramine-O-glucuronide) -based urine LFIA for onchocerciasis, which accurately identified 85% of analyzed patient samples (N = 27).
Also Read: Moxidectin-New Treatment for Onchocerciasis
The new, non-invasive test may provide an inexpensive method of determining in real time whether a person has an infection, which would give public health officials and doctors critical information for tracking outbreaks and treating current infections.
"River blindness affects individuals both in Africa and Latin America, and because many of these endemic regions are difficult to access, what is needed in the field is an inexpensive point-of-care means to monitor the disease," says Dr. Janda.
River blindness is a filarial disease, like elephantiasis, and occurs when the parasitic worm Onchocerca volvulus takes up residence in the skin. Adult worms pump out babies (microfilaria) at an alarming rate, which are ultimately re-spread by blackfly bites. The microfilariae can migrate to the eye and die, releasing toxins and causing inflammation. People with the disease will slowly go blind without medical intervention.
Janda says onchocerciasis monitoring and evaluation are especially necessary steps for people leading elimination efforts. To know if these efforts are working, doctors need to be able to show when disease transmission has been interrupted. The current gold standard for detecting the parasitic worms is a "skin snip" biopsy. However, snips are generally insensitive indicators of infection, and the sensitivity of the skin snip decreases as the density of microfilaria in the skin decreases. Other tests cannot distinguish between past and current infections.
Currently, onchocerciasis elimination programs rely primarily on mass drug administration of the therapy Ivermectin to suppress and eventually eliminate transmission of Onchocerca volvulus. Yet, without a means to evaluate if an infection is ongoing, it's hard to assess if prevention efforts are working -- and if it's safe for people to stop taking medication.
The new lateral flow assay took over 10 years to develop, but it is now ready for manufacturing and testing in the field. The key to the assay's success was in the making of designer antibodies to detect a unique biomarker that only shows up when a human host has metabolized a worm neurotransmitter called tyramine. Humans then secrete this biomarker in urine.
A negative on the "dipstick" test shows a colored line in the test. Got the parasite? The test would show no lines.
Unlike the skin snip biopsy, Janda says this non-invasive test is the first to use a metabolite produced by adult worms. Moreover, the dipstick's inexpensive design, coupled with smartphone apps, would offer automatic image processing, which ultimately could translate to address critical gaps in the surveillance and treatment of river blindness.
For further information log on to 10.1021/acsinfecdis.8b00163

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd