- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
New JAS Guideline for Treatment and Diagnosis of Familial Hypercholesterolemia
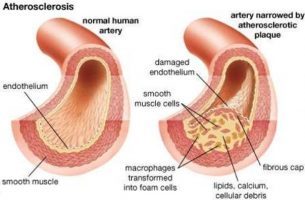
The Japan Atherosclerosis Society has released new guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of familial hypercholesterolemia (FH). The guidelines are published in the Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis.
Mariko Harada-Shiba, Department of Molecular Innovation in Lipidology, National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center Research Institute, and colleagues drafted the guideline.
Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is an autosomal hereditary disease with the 3 major clinical features of hyper-LDL-cholesterolemia, premature coronary artery disease, and tendon and skin xanthomas. As there is a considerably high risk of coronary artery disease, in addition to early diagnosis and intensive treatment, family screening (cascade screening) is required.
Key Recommendations:
- For a diagnosis of FH, at least 2 of the following criteria should be satisfied: LDL-C ≥180 mg/dL, tendon/skin xanthomas, and the history of FH or premature coronary artery disease (CAD) within 2nd-degree blood relatives.
- Intensive lipid-lowering therapy is necessary for the treatment of FH. The first-line drug should be statin.
- Screening for coronary artery disease as well as asymptomatic atherosclerosis should be conducted periodically in FH patients.
- For homozygous FH, consider LDL apheresis and treatment with PCSK9 inhibitors or MTP inhibitors.
- For severe forms of heterozygous FH who have resistant to drug therapy, consider PCSK9 inhibitors and LDL apheresis.
- Refer FH homozygotes as well as heterozygotes who are resistant to drug therapy, who are children or are pregnant or have the desire to bear children to a specialist.
For further reference click on the link: https://doi.org/10.5551/jat.CR003

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd