- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
New compound for treating Prosthetic Joint Infections discovered
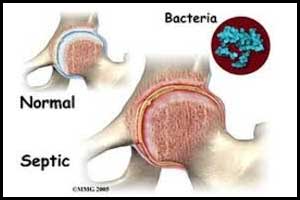
The lead compound PLG0206 has been granted Qualified Infectious Disease Product (QIDP) designation by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of prosthetic joint infections (PJI), announced Peptilogics, a development stage company.PJI is one of the most challenging complications of growing bacteria and a serious, life-threatening condition with few effective treatment options.
PLG0206 is designed with the Company's eCAP (engineered cationic antibiotic peptide) platform that enhances the antimicrobial activity found in naturally occurring peptides and improves the safety profile. eCAPs are being engineered as intravenous (IV) antibiotics with highly amplified activity by targeting and disrupting bacterial membranes. This causes rapid bacterial eradication via chemical imbalance without inducing lysis. Unlike most of the currently approved antibiotics that are effective against actively growing bacteria, eCAPs have shown activity against growing and dormant bacteria
Preclinical studies showed that treatment with PLG0206 eradicated different biofilm-associated bacteria (including methicillin-sensitive [MSSA] and methicillin-resistant [MRSA] Staphylococcus aureus isolates), sterilizing implants after short exposure in a biofilm model.
The data suggested PLG0206 could quickly kill implant-associated biofilm bacteria in a clinical setting. The QIDP designation was created by the Generating Antibiotic Incentives Now (GAIN) Act, which was part of the FDA Safety and Innovation Act of 2012 (FDASIA). QIDP designation provides certain incentives for the development of new antibiotics, including an additional five years of market exclusivity, as well as eligibility for Priority Review and Fast Track designation.
“Researchers estimate that by 2020, more than 65,000 patients per year with prosthetic joint implants will develop PJIs, resulting in over $1.6 billion in annual inpatient costs,” said Sanjay Kakkar M.D., the chief executive officer of Peptidomics. He added,“We are delighted that the FDA has granted PLG0206 QIDP designation, and we look forward to advancing the compound into clinical development later this year.”

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd