- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
New Antimicrobial gel could improve root canal results
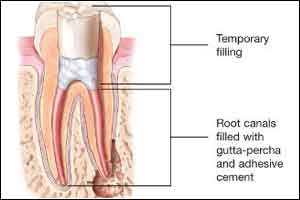
More than 15 million root canals are done each year, according to the American Association of Endodontists. During the procedure, the tooth's pulp and nerve are removed before the tooth is cleaned and sealed. If bacteria, viruses or yeasts contaminate the tooth, another root canal procedure or surgery must be done.
Now, the results of root canal treatments could improve because of an antimicrobial gel discovered and developed at the Indiana University School of Dentistry.
Ghaeth H. Yassen, a visiting assistant professor, has developed an injectable antimicrobial gel that could disinfect a tooth during a root canal procedure.
"I wanted to create a gel that provides sustained antimicrobial properties even when it is removed. I also wanted it to have minimal toxic effect on stem cells and not cause tooth discoloration," he said. "Creating an antimicrobial space is especially important during clinical regenerative endodontic procedures."
Yassen said the gel has advantages over traditional medications, including calcium hydroxide, widely used as an antibacterial agent.
"The gel offers extended and significantly longer residual antibacterial properties, which has been proven in papers published in the Journal of Endodontics and the International Endodontic Journal," he said. "It is biocompatible, and it contains a low concentration of antimicrobial elements."
Yassen said the next steps include optimizing a version of the gel that is opaque to X-rays and other radiation, which will enable dental care professionals to track it within the root canal system.

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd