- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
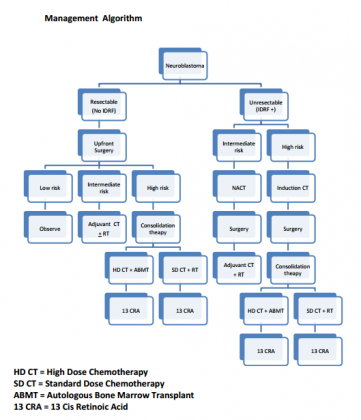
Neuroblastoma- Standard Treatment Guidelines

Introduction
Neuroblastoma is the most common extra cranial solid tumor in children. It arises from neural crest cells which differentiate in cells of the sympathetic ganglia and adrenal medulla. It remains a complex medical challenge with spontaneous regression at one end to an unpredictable clinical course and dismal outcome at the other end of spectrum.
Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India has issued the Standard Treatment Guidelines for Neuroblastoma.
Following are the major recommendations :
Image defined risk factors (IDRF) for Neuroblastoma
Site of primary tumor: Cervical, cervico-thoracic, thoracic, thoraco-abdominal, abdominal, and pelvic.
Local extent:
- Crossing midline
- Encasement of any major vessel at that site like carotid, vertebral, IJV, subclavian, mediastinal great vessels, abdominal aorta and its branches, IVC, iliacs.
- Infiltration of adjacent critical areas like skull base, trachea, main bronchi, brachial plexus, pericardium, , costo-vertebral junction (especially between D9-D12), portahepatis, hepato-duodenal ligament, mesenteric root, sciatic notch, intra-spinal extension (more than 1/3rd diameter of spinal canal involved on axial image or loss of perimedullary space or abnormal cord).
- Infiltration of adjacent organs like heart, diaphragm, liver, kidney, spleen, pancreas, etc.
Presence of multifocal primary
Collections in cavities like pleural or peritoneal
Adenopathy: Enlarged local or distant nodes
Metastatic disease: Bony lesions, Liver or lung lesions
Neuroblastoma risk Stratification
- Risk stratification should be done at a tertiary centre before initiation of therapy.
- In unresectable lesions generous core biopsy (image guided) should be performed for histopathology and molecular studies.
| Risk | Age | Stage | MYCN status | |
| Low | <547 days | 1, 2A/B,4S | NA | |
| > 547 days | 1, 2A/B | NA | ||
| Intermediate | <547 days | 3, 4 | NA | |
| > 547 days | 3 | NA | ||
| High | <547 days | 1, 2, 3, 4, 4S | Amp | |
| > 547 days | 1,2,3 | Amp | ||
| > 547 days | 4 | Any | ||
Guidelines by The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare :
Dr Anil K. D’ Cruz
Director and
Chief Head and Neck Services,
Tata Memorial Hospital, Mumbai
Next Story
NO DATA FOUND

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd