- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
Most Melanomas Not Malignant Transformation of Moles
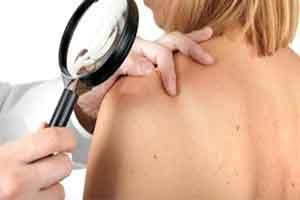
As the summer draws to a close, it's time to start putting away flip-flops, bathing suits and beach bags. But as the seasonal supplies disappear into the back of the closet, sunscreen should stay within arm's reach for year-round protection against the sun's ultraviolet rays.
Because exposure to those harmful UV rays can increase one's risk of skin cancer and people spend a lot of time in the sun during the summer the end of the season is also a good time to perform a skin self-exam. While it's important to look for any suspicious spots on the skin, research published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology indicates that it's vital to check for new growths in order to detect melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer.
After reviewing 38 published studies comprising 20,126 melanomas, researchers found that less than one-third of melanomas (29 percent) arose from an existing mole, while the vast majority (71 percent) appeared on the skin as new spots. Moreover, melanomas that arose from existing moles were thinner than other melanomas, indicating that patients whose melanoma was associated with an established mole had a better prognosis than others.
"These results could indicate that patients who monitor their existing moles for suspicious changes could detect melanoma in its early stages, when it's most treatable," says study author Caterina Longo, MD, PhD, a dermatologist at the University of Modena and Reggio Emilia in Italy. "Because the disease is more likely to appear as a new growth, however, it's important for everyone to familiarize themselves with all the moles on their skin and look for not only changes to those moles, but also any new spots that may appear."
The American Academy of Dermatology encourages everyone to perform regular skin self-exams, asking a partner to help them check hard-to-see areas like the back. Any new or suspicious spots warrant a trip to a board-certified dermatologist, as does anything changing, itching or bleeding.
The AAD also recommends that everyone protect themselves from the sun's harmful UV rays by seeking shade, wearing protective clothing and applying a broad-spectrum, water-resistant sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher. According to additional research published in JAAD today, however, only 39 percent of consumers consider broad-spectrum protection as a factor in choosing a sunscreen.
"People may think SPF is the only important element of sunscreen selection, but that's not the case," says study author Roopal V. Kundu, MD, FAAD, an associate professor of dermatology at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine in Chicago. "SPF only tells you how much protection a sunscreen provides against UVB rays. To be protected against both UVA and UVB rays, both of which can cause skin cancer, you need to use a broad-spectrum sunscreen."
For more information on skin cancer prevention and detection, visit the AAD website SpotSkinCancer.org. There, you can also find instructions on how to perform a skin self-exam, download a body mole map for tracking changes in your skin, and find free SPOTme® skin cancer screenings in your area. SPOT Skin Cancer™ is the AAD's campaign to create a world without skin cancer through public awareness, community outreach programs and services, and advocacy that promote the prevention, detection and care of skin cancer.
For more details click on the link :

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd