- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
Mavacamten, a promising treatment for Obstructive Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
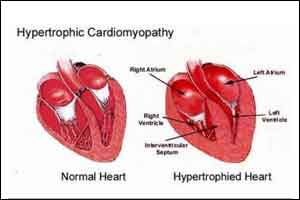
USA: Mavacamten, an orally administered, small-molecule modulator of cardiac myosin, shows promising results for the treatment of obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (oHCM) in a phase 2 study.
The study, published in the journal Annals of Internal Medicine, showed that Mavacamten reduced left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) obstruction and improved exercise capacity and symptoms in patients with obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a disease in which the heart muscle (myocardium) becomes abnormally thick (hypertrophied) that makes it make it harder for the heart to pump blood. Most people with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy have a form of the disease in which the wall (septum) between the two bottom chambers of the heart (ventricles) becomes enlarged and restricts blood flow out of the heart (obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy).
The obstructive phenotype of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) entails left ventricular hypercontractility with left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) obstruction and can result in exercise intolerance, exertional dyspnea, chest pain, or fatigue despite management with negative inotropes like β-blockers and nondihydropyridine calcium channel blockers. The non-FDA-approved drug mavacamten is a small molecule that reduces hypercontractility by inhibiting the binding of β-cardiac myosin to actin.
Stephen B. Heitner, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, Oregon (S.B.H.), and colleagues conducted the study to characterize the effect of mavacamten on left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) gradient.
The researchers conducted a manufacturer-funded, open-label, phase 2 study (PIONEER-HCM; NCT02842242) examining two treatment regimens in 21 symptomatic individuals with obstructive HCM (mean age, 57; 57% men; β-blocker use, 86%). Cohort A received mavacamten at 10 to 20 mg daily without other medications; cohort B received 2 to 5 mg daily and was allowed concomitant β-blockers.
The primary endpoint was a change in postexercise LVOT gradient at 12 weeks.
Also Read: Mitraclip-Mitral valve placation for the treatment of obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Key findings of the study include:
- In cohort A, mavacamten reduced mean postexercise LVOT gradient from 103 mm Hg at baseline to 19 mm Hg at 12 weeks (mean change, −89.5 mm Hg).
- Resting LVEF (left ventricular ejection fraction) was also reduced (mean change, −15%).
- Peak VO2 increased by a mean of 3.5 mL/kg/min.
- In cohort B, the mean postexercise LVOT gradient decreased from 86 mm Hg (SD, 43) to 64 mm Hg (SD, 26) (mean change, −25.0 mm Hg), and mean change in resting LVEF was −6%.
- Peak VO2 increased by a mean of 1.7 mL/kg/min.
- Dyspnea scores improved in both cohorts.
- Mavacamten was well tolerated, with mostly mild (80%), moderate (19%), and unrelated (79%) adverse events.
- The most common adverse events definitely or possibly related to mavacamten were decreased LVEF at higher plasma concentrations and atrial fibrillation.
This study demonstrates impressive improvements in LVOT obstruction, symptoms, and exercise tolerance with a drug from a novel therapeutic class in patients with refractory, symptomatic, obstructive HCM.
The study lacks a control group or blinding but sets the stage for a larger placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 study currently recruiting 220 participants and using an endpoint of improvement in symptoms and exercise tolerance (EXPLORER-HCM; NCT03470545). Success could transform therapy for this difficult condition.
chest paindifficult to treatdifficulty in breathingdyspneaexercise toleranceHeart diseaseheart disordershypertrophic cardiomyopathyleft ventricular ejection fractionleft ventricular outflow tractLVOTLVOT obstructionMavacamtenobstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathyStephen B. Heitner
Source : With inputs from Annals of Internal MedicineNext Story
NO DATA FOUND

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd