- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
Malignancies of Gastroesophageal Junction (Adenocarcinoma GE Junction)-Standard Treatment Guidelines
Introduction
Tumors having their center 5-cm proximal or distal to the anatomic cardia are classified as malignancies of the GE junction.Histologically they can be adenocarcinoma or Squamous Cell Carcinomas.Squamous cell Carcinomas are treated as carcinoma esophagus, hence all the further discussion will be restricted to Adenocarcinoma GE Junction
Incidence of adenocarcinoam GEJunction is on the rise and is emerging as a new disease. Carcinoma esophagus is now more common in the lower third and there is marked increase in the carcinomas of proximal stomach creating the new identity of Adenocarcinoma of GEJunction. There is a rise in the incidence of almost 10% per year, more the non endemic areas or European world.
Unlike Squamous cell carcinoma,Adenocarcinoma GEJunction is found in the developed countries and in patients of upper socio economic status and has a better prognosis than the SCC esophagus. It is associated with Obesity, High Body mass index, GERD and Barrets Esophagus.
Barrets Esophagus-this defined as the presence of intestinal metaplasia (mucin producing goblet cells) in columnar cell lined epithelium that replaces the squamous epithelium of the distal esophagus.This specialized metaplasia confirmed on histopathology is mandatory for diagnosis of barrets Esophagus which confers a 40-125 fold higher risk for developing adenocarcinoma GEJunction and is the singlemost important risk factor. Classification of Barrets Esophagus.
Siewart's Classification
Type I -Epicenter of tumour or more than 66% of the tumor mass located >1 cm above the anatomic GE junction
Type II- Tumor epicenter located within 1-cm proximal and 2-cm distal to the GE junction
Type III- Tumor epicenter or more than 66% of the tumor mass is located more than 2 cm below the anatomic GE junction
Revised Seiwart's classification of 2000
Type I adenocarcinoma, which may infiltrate the GE junction from above
Type II adenocarcinoma, which arises from the GE junction
Type III adenocarcinoma, or subcardial gastric carcinoma, which infiltrates up to the GE junction from below
Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India has issued the Standard Treatment Guidelines for Malignancies of Gastroesophageal Junction (Adenocarcinoma GEJunction).
Following are the major recommendations :
WHEN TO SUSPECT
Presenting Symptoms
The most common presenting feature of adenocarcinoma GEJunction is dysphagia, initially to solids and then to liquids. Other symptoms that patient may present with are
- Odynophagia
- Dyspepsia
- Loss of weight
- Anorexia
- Left supraclavicular node
- Haematemesis
- Vomiting
Differential Diagnosis
All elderly patients presenting with long standing dyspepsia and features of GERD or with anorexia, loss of weight and dysphagia,should be investigated for carcinoma esophagus Common differential diagnosis are
- GERD
- Barrets Esophagus
- Cercinoma Stomach
- Carcinoma Esophagus
- Achlasia cardia
- Hiatus Hernia
- Esophageal diverticulum or stricture
Examination
Besides the routine general and systemic examination, patient should be assessed for
- General condition
- Nutritional status
- Pallor
- Left supraclavicular node
WORKUP FOR DIAGNOSIS AND STAGING
Investigations-
Following investigations are mandatory for assessing any suspected or diagnosed case of Carcinoma Esophagus
Upper GI Endoscopy –To see for
- Presence of growth
- Site of growth
- Nature of growth
- Vertical and circumferential extent of growth
- Passage of scope beyond the growth 69
- Status of stomach
- Presence of Barrets esophagus
( Naso gastric feeding tube to be placed if esophageal lumen found to be
obstructed)
Endoscopic Biopsy- from representative site. Following to be assessed
- Histology
- Differentiation
- Presence of Barrets esophagus
CECT Chest and upper abdomen-To see for
- Vertical and Horizontal extent of diseases
- Adherence or infiltration of surrounding structures like trachea, main bronchus,aorta and pericardium
- Para esophageal nodes
- Involvement of GE Junction and proximal stomach in the lower third esophageal
and GEJunction cancers - Liver metastasis
- Pericardial and plural effusion
- Ascitis
- Perigastric lymphnodes
- FNAB of left supraclavicular node if present and left scalene pad of fat biopsy if
nodularity felt - Hb, TLC, DLC, blood grouping
- Biochemistry-LFT,RFT, Blood Sugar, Electrolytes and platelets
- ECG
- Ba Swallow-
Optinal Investigations
Following Investigations are optional and may be done in tertiary care centres where
facilities are available
- Endoscopic Ultrasound
- Endoscopic ultrasonographic FNAB of paraesophageal nodes
- PET Scan
- Her 2 Ney receptor study by FISH technique on biopsy specimen
STAGING (AJCC 7th Ed 2010)
- Tis High grade dysplasia (ca in situ)70
- T1a Tumour invades lamina propria or muscularis mucosa
- T1b Tumour invades submucosa
- T2 Tumour invades muscularis propria
- T3 Tumour invades adventitia
- T4a Resectable tumour invading pleura, pericardium or diaphragm
- T4b Unresectable tumour invading other adjacent structures,
- Nx Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed
- N0 No regional lymph node metastasis
- N1 Metastasis in 1-2 regional lymph nodes
- N2 Metastasis in 3-6 lymph nodes
- N3 Metastasis in seven or more regional lymph nodes
- M0 No Metastasis
- M1 Distant Metastsis
Group staging
| Stage | T | N | M |
| 0 | T1 | N0 | M0 |
| 1A | T1 | N0 | MO(G1,2) |
| 1B | T1 T2 | N0 N0 | M0(G3) M0(G1,2) |
| IIA | T2 | N0 | M0(G3) |
| IIB | T3 T1-2 | N0 N1 | M0 M0 |
| IIIA | T1-2 T3 T4a | N2 N1 N0 | M0 M0 M0 |
| IIIB | T3 | N2 | M0 |
| IIIC | T4a T4b Any | N1-2 Any N3 | M0 M0 M0 |
| IV | Any | Any | M1 |
TREATMENT
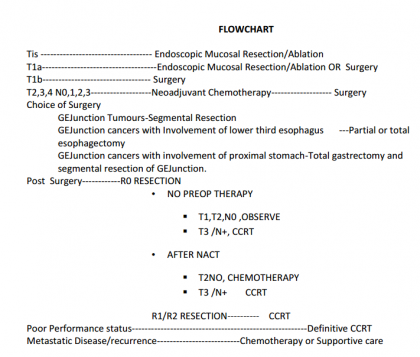
Neoadjuvant Therapy-All patients with growths T2N0 and beyond should receive 4 # of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy with two drug regime of any combination including platinum and taxane based drugs can be used too
Surgery-Surgery remains the gold standard in treatment of carcinoma GEJunction Since Surgery involves thoracic surgery and post operative critical care, treatment of GEJunctionmalignancies should be undertaken where facilities and expertise for thoracic surgery and critical care are available
Contraindications to Resection-Surgical resection should not be considered in the following circumstances
- T4b lesion
- Left supra-clavicular node
- Distant metastasis
- Multi-station bulky nodal mass
- Poor general condition
- Co-morbid medical conditions making patient unfit for anesthesia
Treatment
Treatment of Barrets esophagus
Low grade and High grade dysplasia and Metaplasia can be observed, however Barrets esophagus needs active treatment and close follows. Barrets Esophagus can be treated with Proton Pump inhibiters, Treatment of H pylori infection, Cox Inhibiters. Surgery for GERD and Hiatus hernia prevent formation and progress of Barrets esophagus and in certain circumstances when the segment is large or persistent and progressing then surgical management with resection may have to be resorted to
Treatment of Adenocarcinoma GE Junction
Preoparative laproscopy may be undertaken before the definitive surgery to assess operability
Segmantal Resection-The involved Segment can be excised with a margin of 5 cms through a left thoraco abdominal incision,running along the left 7th rib,upto the umbilicus (Sweet-Garloch incision) Continuity is maintained with gastro esophagectomy and D2 nodal dissection is done with the resection of the involved segment.This procedure can only be undertaken if the growth is below the diaphragmatic hiatus.Anastamosis can be done handsewn or stapled.
Partial Esophagectomy (Ivor-Lewis Procedure)
This procedure is performed for cancers of the GEJunction invoving the lower third of the esophagus with a right thoracotomy and upper midline laparotomy incision. The lower third of esophagus is excised with a margin of 5 cms and anastamosis done with the gastric tube is done in the mediastinum.Mobolization of stomach,formation of gastric tube and nodal dissection remain the same as for segmental esophagectomy
Total Esophagectomy with two field nodal dissection to avoid a mediastinal anastamosis,Total esophagectomt can be performed for GEJunction cancers involving the lower third oesophagus. This includes the removal of complete esophagus, removal of paraesophageal lymphnodes and D2 dissection of gastric lymphnodes, and using a stomach tube as conduit to restore continuity with anastamosis with cervical esophagus in the left side of the neck. This can be done by following two procedures
- Transthoracic Total Esophagetomy (TTE), which includes a right posterolateral thoracotomy for mobilization of esophagus and paraesophageal nodal dissection ,mobilization of stomach with D2 nodal dissection of gastric lymph nodes ,total esophagectomy, gastric mobilization and formation of gastric tube through a upper midline laparotomy incision and pulling up the gastric tube and anastamosing with proximal esophagus in the left side of the neck.A minimum of 15 nodes should be dissected for adequate nodal dissection.Mobilisation of the esophagus can also be done by VATS( Video Assisted Thoracic Surgery)
- Transhiatal Total esophagectomy(THE) -Is a two step procedure where the thoracotomy is excluded and the esophagus is mobilized blindly thorugh transehiatal route.Adequate paraesophageal nodal dissection is not possible through this procedure,however it avoids a thoracotomy.
Total Gastrectomy with excision of lower third esophagus-Siewert's Type three carcinomas of GEJunction which extend into proximal stomach are treated with total gastrectomy and excision of lower esophagus through a thoraco abdominal incision.Nodal Diseection remains the same nad continuity is restored with esophagojejunostomy.
Early Carcinoma of GEJunction-It is rare to find early cases of cancer GEJunction in india,however small T1 lesions can be treated by any of the following procedures
- Endoscopic mucosal resection
- Endoscopic submucosal resection
- Radiofrequency ablation
- Photodynamic therapy
- Cryotherapy 73
- Local excision
Histopathological Examination-Opertaive specimen should be examined for the following
- Histology
- Grade
- Margins
- Depth of invasion
- Involvement of extra esophageal tissue
- Lymphovascular invasion
- Number of nodes dissected
- Number of nodes involved
- Perinodal & Perineural infiltration
- Her-2 Neu by FISH in metastatic disease
Adjuvant therapy-
R0 RESECTION
• NO PREOP THERAPY
- T1,T2,N0 ,OBSERVE
- T3 /N+, CCRT
• AFTER NACT
- T2NO, CHEMOTHERAPY
- T3 /N+ CCRT
R1/R2 RESECTION CCRT
Management of Unresectable tumors or of patients with poor performance status
Definitive CCRT-Concurrent Radiotherapy with 6000Gy of radiotherapy with either of the following combination of drugs.
- Cisplatin and 5FU
- Paclitaxel/Docetaxel with 5FU
Management of Metastatic disease- Metastatic disease is managed with single or two drug regime using chemotherapy platinum,taxanes and 5-FU or supportive care. TRANSTUZUMAB (Herceptine)can be used for HER2 neu + cases
Paliative Care
Obstruction
- Endoscopic lumen restoration
- Laser excision
- Endoscopic lumen enhancement
Expandable stents
Wire guided balloon dilatation
- Surgical placement of gastrostomy or jejunostomy tube
- Palliative Chemotherapy
BLEEDING
- Endoscopic intervention
- EBRT
PAIN
- Local blocks
- Painkilllers
FOLLOWUP
All patients of GEJunction to be followed regularly after completion of treatment, to look for
- Anastamotic Stricture
- Anastamotic recurrence
- Local recurrence
- Nodal recurrence
- Distant Metastasis ( Liver and lung)
Frequency of follow-up-Once in every three months for two years and then six monthly till five years post treatment, followed by annual review, lifelong
Following Investigation sto be done at Review
- Hb,TLC,DLC
- LFT
- X-ray chest
- USG Abdomen75
- UGI Scopy ,once in a year
- CECT Chest( Optioanl,without any symptoms)
Prevention
- Avoid alcohol and High calori diet
- Avoid obesity
- Treat GERD
- Tretament of Barrets esophagus
Guidelines by The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare :
Col (Prof) Sanjay Kapoor VSM,
HOD Oncology Command Hospital Lucknow

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd