- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
Low vitamin D increases diabetic retinopathy
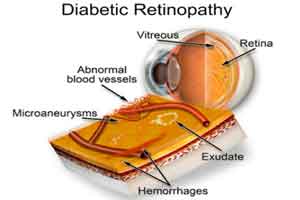
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is among the most common diabetic complications and is the leading cause of blindness among working-aged individuals worldwide.Previous studies have shown an inverse association between Vitamin D Deficiency and Diabetic Retinopathy in various populations but this association has not been studied in Indian population. Dr. Ashinne B at Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina and associates have conducted a retrospective study and found that Low level of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) is associated with increased severity of diabetic retinopathy (DR) in Asian Indians with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The study also found that vitamin D deficiency (VDD) is associated with a 2-fold increased risk for proliferative DR (PDR).The new study has been published in the journal Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.
Researchers in this retrospective study analyzed medical records of 3054 patients with T2DM (age, >18 years) who underwent detailed retinal examination with DR severity grading. DR grades were classified as no DR, mild nonproliferative DR (NPDR), moderate NPDR, severe NPDR, or PDR. They compared serum (25(OH)D) levels between patients with DR and those without DR.
Overall, 69.4% of patients had 25(OH)D levels <20 ng/mL. Serum 25(OH)D level was significantly lower in patients with DR vs those without DR (11.9±2.2 ng/mL vs 13.7±2.1 ng/mL; P<.001). After adjustment for confounders, VDD was associated with 2-fold increased risk for PDR (OR, 2.05; 95% CI, 1.35-3.11; P=.001).
“Our finding contributes supporting evidence to a protective role of vitamin D on the development of DR, particularly at the most advanced end of the spectrum,’’ the authors wrote. Considering the high prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and the burden of the diabetic retinopathy, screening type 2 diabetes patients who are at risk of vitamin D deficiency should be considered in Indian population.
The authors have called for further studies to evaluate the role of vitamin D supplementation in the treatment of DR.
For further reference log on to : DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2018.02.040
blindnessdiabetic retinopathyDuke University School of Medicinehydroxyvitaminjournal Diabetes Research and Clinical PracticeLow level of serumlow vitamin DretinopathyType 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Type-2 diabetesVitamin D deficiencyVitamin D Supplementation
Source : With inputsNext Story
NO DATA FOUND

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd