- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
ICMR Antimicrobial guidelines in immunecompromised hosts and solid organ transplant recipients

With advances in treatment of organ failure, auto-immune diseases and malignancies, an increasing population of immune compromised hosts and transplant recipients will develop infections and require care by the medical system. Such patients present unique challenges with regard to diagnosis and treatment, which often differ from the immune competent host. Moreover, these patients are likely to suffer repeated episodes of infections and consequently receive repeated courses of antimicrobial agents leading to higher level of antimicrobial resistance in pathogens.
Indian Council of Medical Research, Department of Health Research has issued the ICMR Antimicrobial guidelines in immunecompromised hosts and solid organ transplant recipients. Following are the major recommendations :
Case definition
An immune compromised host includes the following:
- recipients of solid and stem cell organ transplants
- congenital immune deficiency disorders
- patients on medications that compromise cell mediated immunity eg corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, mTOR pathway inhibitors, TNF-alpha antagonists, anti-thymocyte globulin and monoclonal antibodies like rituximab, adalimumab, etc.
- Patients suffering from cancer, cystic fibrosis
Common pathogens
Immunocompromised hosts are at risk of developing opportunistic infections but also remain exposed to normal community acquired pathogens. Clinical presentation can be subtle and often difficult to diagnose in these hosts. The pathogens involved are by and large the same as those affecting immune competent hosts. Some specific pathogens unique to patients with compromised cell mediated immunity include Listeria monocytogenes, Nocardia spp, Pneumocystis jiroveci, Cytomegalovirus (CMV), Cryptococcus, Aspergillus spp, Strongyloides stercoralis
Prevalent AMR status in common pathogens
Table 1. Enterobacteriaceae isolates from blood. ICMR AMR data 2014.
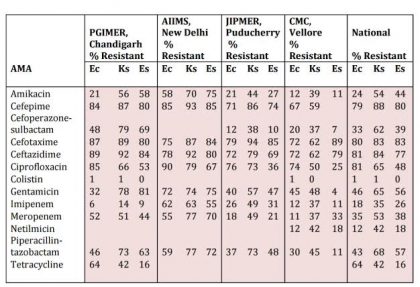
Note : Ec : Escherichia coli; Ks : Klebsiella spp.; Es : Enterobacter spp
Table 2. Salmonella Typhi isolates from blood ICMR AMR Data 2014
| AMA | PGIMER, Chandigarh ‘n’ 109 No. R (%) | AIIMS, New Delhi ‘n’ 22 No. R | CMC, Vellore ‘n’ 71 No. R (%) | JIPMER, Puducherry ‘n’ 7 No. R | National ‘n’ 209 No.R %) |
| Ampicillin | 9 (8.3) | 0 | 2 (2.8) | 0 | 11 (5.3) |
| Cefixime | 0 (0) | 0 | 0 (0) | 0 | 0 (0) |
| Ceftriaxone | 0 (0) | 0 | 0 (0) | 0 | 0 (0) |
| Chloramphenicol | 3 (2.8) | 0 | 1 (1.4) | 0 | 4 (1.9) |
| Ciprofloxacin | 56 (51.4) | 15 | 67 (94.4) | 7 | 145 (69.4) |
| Trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole | 0 (0) | 0 | 3 (4.2) | 0 | 3 (1.4) |
Note : If No. Tested is ≥30, No. R (%) given. If No. tested <30, only No. R given.
Table 3. Staphylococcus aureus ICMR AMR Data 2014
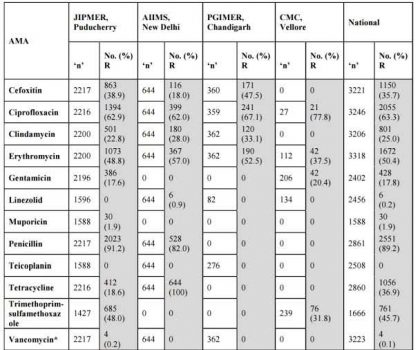
*The 4 numbers listed as Vancomycin Resistant (R) are VISA isolates.
No VRSA was isolated during the year 2014 at JIPMER.
Cefoxitin : Surrogate marker for Methicillin.
Table 4. Enterococcus faecalis ICMR AMR Data 2014
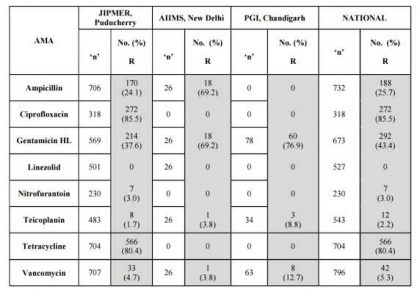
Table 5. Enterococcus faecium ICMR AMR Data 2014.
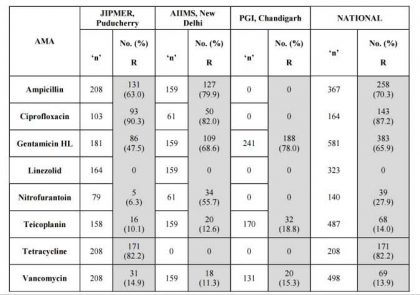
Table 6. Pseudomonas aeruginosa ICMR AMR Data 2014
| AMA | PGIMER, Chandigarh ‘n’ 75 R (%) | AIIMS, New Delhi ‘n’ 102 R (%) | JIPMER, Puducherry ‘n’ 113 R (%) | CMC, Vellore ‘n’ 84 R (%) | National ‘n’ 374 R % |
| Amikacin | 27 | 49 | 38 | 21 | 35 |
| Aztreonam | 62 | 55 | 30 | 48 | |
| Cefepime | 52 | 57 | 20 | 41 | |
| Cefoparazone -sulbactam | 39 | 41 | 30 | 38 | |
| Ceftazidime | 64 | 51 | 51 | 23 | 47 |
| Colistin | 34 | 2 | 10 | ||
| Imipenem | 17 | 54 | 48 | 25 | 37 |
| Levofloxacin | 44 | 42 | 23 | 36 | |
| Meropenem | 74 | 41 | 23 | 47 | |
| Netilmicin | 66 | 45 | 22 | 45 | |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 44 | 67 | 25 | 46 | |
| Tobramycin | 56 | 43 | 18 | 33 |
Table 7. Acinetobacter baumannii susceptibility pattern 2014
| AMA | PGIMER, Chandigarh ‘n’ 209 R (%) | AIIMS, New Delhi ‘n’ 143 R (%) | JIPMER, Puducherry ‘n’ 157 R (%) | CMC, Vellore ‘n’ 90 R (%) | National ‘n’ 599 R % |
| Amikacin | 77 | 83 | 59 | 84 | 75 |
| Aztreonam | 87 | 93 | 84 | 87 | |
| Cefepime | 98 | 86 | 75 | 61 | 81 |
| Cefoparazone -sulbactam | 89 | 23 | 22 | 47 | 57 |
| Ceftazidime | 99 | 86 | 68 | 68 | 84 |
| Colistin | 1 | 64 | 22 | 22 | |
| Imipenem | 52 | 83 | 62 | 64 | 63 |
| Levofloxacin | 86 | 68 | 60 | 73 | |
| Meropenem | 50 | 86 | 59 | 61 | 62 |
| Netilmicin | 79 | 56 | 69 | ||
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 73 | 86 | 71 | 83 | |
| Tobramycine | 61 | 52 | 55 | ||
| Tobramycin | 54 | 64 | 58 | 58 | |
| Trimethoprim-sulphamethoxa zole | 46 | 63 | 55 |
Table 8 Central nervous system infections
| Clinical condition | Common pathogens | Empiric antimicrobial agents | Alternative antimicrobial agents | Comments |
| Acute bacterial meningitis | Pneumococcus, Listeria monocytogenes, H.influenzae, Meningococcus | Ceftriaxone 2 gm IV q 12h/ Cefotaxime 2 gm IV q 4-6h + Ampicillin 2gm IV q4h | Moxifloxacin 400mg IV q 24h or Meropenem 2gm IV q 8h | Exclude TB, Cryptococcus Vancomycin not required due to low level of penicillin resistance in Pneumococcus If penicillin allergic, use cotrimoxazole 15 mg/kg/day (TMP component) or meropenem 2gm IV q 8h to cover for Listeria Duration: 10-14 days, 21 days for Listeria or Gram negative infection |
| Brain abscess, subural empyema | Streptococci, Bacteroides, Enterobacteriace -ae, Staph aureus Nocardia spp | Ceftriaxone 2 gm IV q12h/ Cefotaxime 2 gm IV q 4-6h + Metronidazole 1 gm IV q 12h Duration based upon clinical & radiological response, minimum 8 weeks Co-trimoxazole 15 mg/kg/dose (trimethoprim component) IV or PO, plus imipenemcilastatin 500 mg q6h | Meropenem 2gm IV q 8h Linezolid 600 mg IV or PO q12h | Exclude TB, Nocardia, Aspergillus Aspiration/surgical drainage required unless abscess <2.5cm & patient neurologically stable Duration: 3-6 weeks of IV therapy, followed by 12 months of oral therapy |
Table 9 Respiratory tract infections
| Condition | Organisms | Empiric antibiotics | Alternative antibiotics | Comments |
| Pneumonia | S. pneumoniae, H.influenzae, Legionella, E.coli, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas, S.aureus Pneumocystis | Ceftriaxone 2 g IV od or Piperacillin-tazobactam 4.5 gm IV q 6h plus either azithromycin 500 mg PO/IV OD or doxycycline 100 mg PO BD Duration 5-8 days Cotrimoxazole (trimethoprim component 15 mg/kg /day) Duration: 14 days, 21 days in patients with HIV | Imipenem- cilastatin 500 mg q6h Clindamycin 600 mg IV q8h+ Primaquine 15 mg q12h(if sulpha allergy) | If MRSA is a concern, add linezolid 600 mg IV/PO BD Avoid fluoroquinolones unless TB excluded Exclude TB, influenza, Nocardia, fungi (Aspergillus, Mucor, Cryptococcus), Strongyloides hyperinfection De-escalate to narrow spectrum agent on receipt of senstivity report |
| Lung abscess, empyema | Pneumococcus, Strep milleri group, E.coli, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas, S.aureus, anaerobes | Piperacillin-tazobactam 4.5 gm IV q 6h Duration: 3-4 weeks | Cefoperazone-sulbactam 3 gm IV q 12h + clindamycin 600-900 mg IV q 8h | Drainage of pleural space essential for empyema |
| Acute bacterial pharyngitis | Group A ß- hemolytic streptococci (GABHS) | Benzathine penicillin 12 laks units IM or amoxicillin 500 mg PO q8h for 10 days | Most cases viral, confirm GABHS on culture before treating | |
| Head and neck space infections | Polymicrobial (Str pyogenes, Staph aureus, oral anaerobes) | Clindamycin 600 mg IV q8h or Amox-clav 1.2 gm IV/PO q8h | Piperacillin-tazobactam 4.5 gm IV q 6h | Duration: At least 1 week |
| Acute sinusitis | Viral, S.pneumoniae, H.influenzae, M. catarrhalis | Amox-clav 1.2 gm IV/PO q8hfor 7 days | Piperacillin-tazobactam 4.5 gm IV q 6h | Exclude fungi (Aspergillus, Mucor) |
| Acute bronchitis | Viral | - | - | Antibiotics not required |
Table 10 Gastrointestinal & intra-abdominal infections
| Condition | Organisms | Empiric antibiotics | Alternative antibiotics | Comments |
| Acute gastroenteritis Food poisoning | Viral, entero toxigenic & entero pathogenic E. coli S. aureus, B. cereus, C. botulinum | none | none | Rehydration (oral/IV) essential |
| Cholera | V.cholerae | Doxycycline 300 mg PO stat | Azithromycin 1 gm PO stat or Ciprofloxacin 500 mg BD for 3 days | Rehydration (oral/IV) essential Antibiotics are adjuvant therapy |
| Bacterial dysentery | Shigella, Campylobacter, non typhoidal salmonellosis, Shiga toxin producing E. coli | Ceftriaxone 2 gm IV OD for 5 days | Azithromycin 1 gm od x 3d | |
| Amoebic dysentery | E. histolytica | Metronidazole 500 to 750 mg IV q8h for 7-10 days | Tinidazole 2 gm PO OD for 3 days | Add diloxanide furoate 500 mg tds for 10d |
| Enteric fever | S.Typhi, S.Paratyphi A | Outpatients: TMP-SMX4 1 DS tablet BD for 2 weeks or azithromycin 500 mg BD for 7 days | Inpatients: Ceftriaxone 2 g IV OD for 2 weeks | |
| Biliary tract infections (cholangitis, cholecystitis) | Enterobacteriacea (E.coli, Klebsiella) | Piperacillin-tazobactam 4.5 gm IV q 6h or Cefoperazone-sulbactam 3 gm IV q 12h or Ertapenem 1 gm IV OD | Imipenem-cilastatin 500 mg q6h or meropenem 1 gm IV q8h | Surgical or endoscopic intervention to be considered if there is biliary obstruction. De-escalate to narrow spectrum agent on receipt of sensitivities. |
| Hospital acquired diarrhea | C. difficile | Mild-moderate: Metronidazole 400 mg po qid for 10 days Severe: vancomycin 250 mg po q 6h empirically | Confirm by PCR or GDHEIA test | |
| Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis | Enterobacteriaceae (E.coli, Klebsiella) | Piperacillin-tazobactam 4.5 gm IV q 6h or Cefoperazone-sulbactam 3 gm IV q 12h or Ertapenem 1 gm IV OD Duration: 7-10 days | Imipenem-cilastatin 500 mg IV q6h or meropenem 1 gm IV q8h | De-escalate to narrow spectrum agent on receipt of sensitivities. |
| Secondary peritonitis, intra-abdominal abscess | Enterobacteriaceae (E.coli, Klebsiella), Bacteroides | Piperacillin-tazobactam 4.5 gm IV q 6h or Cefoperazone-sulbactam 3 gm IV q 12h or Ertapenem 1 gm IV OD | Imipenem-cilastatin 500 mg IV q6h or meropenem 1 gm IV q8h | Source control is important. De-escalate to narrow spectrum agent on receipt of sensitivities. |
Table 11 Skin & soft tissue infections
| Condition | Organisms | Empiric antibiotics | Alternative antibiotics | Comments |
| Cellulitis | Strep. pyogenes, S.aureus | Cefazolin 2 gm IV q8h. | Clindamycin 600-900 mg IV q8h | Duration: 5-7 days. Can switch to oral therapy once improving |
| Abscess, carbuncle | S.aureus | Cefazolin 2 gm IV q8h | Clindamycin 600-900 mg IV TDS or Linezolid 600 mg q 12h | Get pus cultures. MRSA coverage advisable for children <5 or severe infections |
| Necrotizing fasciitis | Strep. pyogenes, Staph aureus (monomicrobial), Anaerobes, Enterobacteriaceae (polymicrobial) | Piperacillin-tazobactam 4.5 gm IV q 6h or Cefoperazone-sulbactam 3 gm IV q 8h plus Clindamycin 600-900 mg IV q8h | Imipenem-cilastatin 500 mg IV q6h or meropenem 1 gm IV q8h + Clindamycin 600-900 mg IV q8h | Early surgical intervention crucial. De-escalate to narrow spectrum agent on receipt of sensitivities. |
Table 12 Urinary tract infections
| Condition | Organisms | Empiric antibiotics | Alternative antibiotics | Comments |
| Cystitis | Enterobacteriaceae (E.coli, Klebsiella) | Nitrofurantoin 100 mg BD for 5 days | Co-trimoxazole DS BD or ciprofloxacin 500 mg BD for 3 days | Obtain urine cultures before antibiotics & modify therapy based on senstivity report |
| Acute pyelonephritis | Enterobacteriaceae (E.coli, Klebsiella) | Piperacillin-tazobactam 4.5 gm IV q 6h or Cefoperazone-sulbactam 3 gm IV q 12h or Ertapenem 1 gm IV OD. Treat for 10-14 days. | Imipenem-cilastatin 500 mg IV q6h or meropenem 1 gm IV q8h | Obtain urine cultures before antibiotics & switch to a narrow spectrum agent based on senstivity report |
| Acute prostatitis Chronic bacterial prostatitis | Enterobacteriaceae (E.coli, Klebsiella) Enterobacteriaceae (E.coli, Klebsiella) | Piperacillin-tazobactam 4.5 gm IV q 6h or Cefoperazone-sulbactam 3 gm IV q 12h or Ertapenem 1 gm IV OD or Ciprofloxacin 750 mg po bid | TMP/SMX DS PO q12h | Obtain urine and blood cultures before antibiotics & switch to narrow spectrum agent based on sensitivities. Treat for 4 weeks. Therapy based on urine and prostatic massage cultures obtained before antibiotics. Treat for 4-6 weeks |
Table 13 Bone & joint infections
| Condition | Organisms | Empiric antibiotics | Alternative antibiotics | Comments |
| Acute osteomyelitis, septic arthritis | S.aureus, Strep. pyogenes, Enterobacteriaceae | Cefazolin 2 g IV q8h or Ceftriaxone 2 g IV od | Piperacillin-tazobactam 4.5 gm IV q 6h or Cefoperazone-sulbactam 3 gm IV q 12h plus Clindamycin 600-900 mg IV TDS | Treat based on culture of blood/synovial fluid/bone biopsy. Surgical debridement essential. Duration: 3-4 weeks (from initiation or last major debridement) |
| Chronic osteomyelitis, chronic infective arthritis | No empiric therapy | Definitive treatment guided by bone/synovial biopsy culture. |
Table 14 Severe sepsis and septic shock of undetermined source
| Condition | Organisms | Empiric antibiotics | Comments |
| Community acquired | Enterobacteriace ae, Pseudomonas, Staph aureus | Imipenem- cilastatin 1 g IV q8h or meropenem 1 g IV q8h | Add vancomycin if Staph aureus is a concern. Add colistin if high local prevalence of carbapenem resistant organisms or previously colonized. |
| Hospital acquired | Entero-bacteriaceae, Pseudomonas, Acinetobacter, Staph aureus | Imipenem 1g IV q8h or meropenem 1g IV q8h plus Vancomycin 1g IV q12h plus Colistin 9 mu IV stat then 4.5 mu IV q12h | Broaden spectrum if prior antibiotic exposure. De-escalate to narrow spectrum agent on receipt of sensitivities. |
Table 15 Post-op infections following solid organ transplant (kidney, liver, heart, lung)
| Condition | Organisms | Empiric antibiotics | Alternative antibiotics | Comments |
| Post-op fever with hemodynamic stability | Usually not due to infection | None | Look for hematoma, DVT, transfusion related fever, rejection | |
| Surgical site infection | Staph aureus, Entero-bacteriaceae, Pseudomonas | Treat based on culture and sensitivities | ||
| VAP/HAP | Entero-bacteriaceae, Pseudomonas, Acinetobacter | Piperacillin-tazobactam 4.5 g IV q6h or Cefoperazone-sulbactam 3 g IVq8h. Add colistin if high local prevalence of carbapenem resistant organisms. | Imipenem-cilastatin 1g IV q8h or meropenem 1g IV q8h | De-escalate to narrow spectrum agent on receipt of sensitivities. |
| CLABSI | Entero-bacteriaceae, Pseudomonas, Acinetobacter, Staph aureus | Piperacillin-tazobactam 4.5 g IV q6h or cefoperazone-sulbactam 3 g IVq8h plus vancomycin 1g IV q12h. Add colistin if high local prevalence of carbapenem resistant organisms. | Imipenem-cilastatin 1g IV q8h or meropenem 1g IVq8h | Obtain blood cultures before starting antibiotics. Deescalate to narrow spectrum agent on receipt of sensitivities. |
| CA-UTI | ntero-bacteriaceae, enterococci | Piperacillin-tazobactam 4.5 g IV q6h or cefoperazone-sulbactam 3 g IVq12h | Imipenem-cilastatin 1g IV q8h or meropenem 1g IV q8h | Obtain blood and urine cultures before starting antibiotics. Deescalate to narrow spectrum agent on receipt of sensitivities. |
Guidelines by Indian Council of Medical Research :
Dr Soumya Swaminathan, Director General, Indian Council of Medical Research Secretary, Department of Health Research

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd