- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
Gouty Arthritis - Standard Treatment Guidelines
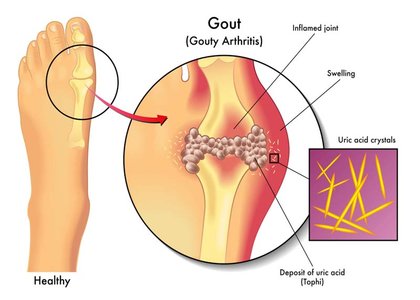
Gout characterized by recurrent attacks of acute inflammatory arthritis— a red, tender, hot, swollen joint. The metatarsal-phalangeal joint at the base of the big toe is the most commonly affected (approximately 50% of cases). However, it may also present as tophi, kidney stones, or urate nephropathy. It is caused by elevated levels of uric acid in the blood which crystallize and are deposited in joints, tendons, and surrounding tissues.
Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India has issued the Standard Treatment Guidelines for Gouty Arthritis. Following are the major recommendations :
Case definition:
Affluent males are the usual victims. It very rarely affects premenopausal women & such a patient should be viewed with suspicion if a diagnosis of gout is made.
Gout can present in a number of ways, although the most usual is a recurrent attack of acute inflammatory arthritis. The metatarsalphalangeal joint at the base of the big toe is affected most often, accounting for half of cases. Other joints, such as the heels, knees, wrists and fingers, may also be affected. Joint pain usually begins over 2– 4 hours and during the night. Other symptoms that may occur along with the joint pain include fatigue and a high fever.
Long-standing elevated uric acid levels (hyperuricemia) may result in other symptomatology, including hard, painless deposits of uric acid crystals known as tophi. Extensive tophi may lead to chronic arthritis due to bone erosion. Elevated levels of uric acid may also lead to crystals precipitating in the kidneys, resulting in stone formation and subsequent urate nephropathy.
Incidence of The Condition In Our Country
Gout affects around 1–2% of the Western population at some point in their lifetimes, and is becoming more common. A number of factors have been found to influence rates of gout, including age, race, and the season of the year. In men over the age of 30 and women over the age of 50, prevalence is 2%
Differential Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis of Gout include
1. Septic Arthritis
2. Pseudo Gout
3. Rheumatoid Arthritis
Prevention And Counseling
Both Dietary and lifestyle changes can decrease uric acid levels.
i. reducing intake of food such as meat and seafood,
ii. consuming adequate vitamin C,
iii. limiting alcohol and fructose consumption
iv. avoiding obesity.
v. Coffee, but not tea, consumption is associated with a lower risk of gout.
Optimal Diagnostic Criteria, Investigations, Treatment & Referral Criteria
SITUATION 1: At Secondary Hospital / Non Metro situation : Optimal standards of Treatment in situations where technology and resources are limited
Clinical Diagnosis :
Usual presentation is acute inflammatory arthritis—a red, tender, hot, swollen joint. The metatarsal-phalangeal joint at the base of the big toe is the most commonly affected (approximately 50% of cases). However, it may also present as tophi, kidney stones, or urate nephropathy. It is caused by elevated levels of uric acid in the blood which crystallize and are deposited in joints, tendons, and surrounding tissues.
Investigations:
1. X Ray
2. Serum Uric Acid Level (Suggestive; to be confirmed by 3 below)
3. MSU crystals in Synovial fluid and tophi (Essential for diagnosis)
4. Complete Blood Picture
5. ESR
6. CRP
7. Renal function test
Treatment:
not applicable
Standard Operating procedure
In Patient
1. Surgery
- Excision of symptomatic tophi
Out Patient
1.Acute Attack
- NSIADS
- Colchicine
- Steroids
2. Chronic (No role in acute attack)
- Allopurinol
- Febuxostat
- Probenacid
3. Physical Therapy
Day Care
1. Injectable medications
2. Intra articular Steroid Injection
Referral criteria:
For further evaluation and management of cases not responding to conventional therapy.
SITUATION 2: At Super Specialty facility in Metro Location where higher end technology is available
Clinical Diagnosis :
Usual presentation is acute inflammatory arthritis—a red, tender, hot, swollen joint. The metatarsal-phalangeal joint at the base of the big toe is the most commonly affected (approximately 50% of cases). However, it may also present as tophi, kidney stones, or urate nephropathy. It is caused by elevated levels of uric acid in the blood which crystallize and are deposited in joints, tendons, and surrounding tissues.
Investigations:
1. X Ray
2. Serum Uric Acid Level (Suggestive; to be confirmed by 3 below)
3. MSU crystals in Synovial fluid and tophi (Essential for diagnosis)
4. Complete Blood Picture
5. ESR
6. CRP
7. Renal function test
Treatment:
not applicable
Standard Operating procedure
In Patient
1. Surgery
- Excision of symptomatic tophi
Out Patient
1.Acute Attack
- NSIADS
- Colchicine
- Steroids
2. Chronic (No role in acute attack)
- Allopurinol
- Febuxostat
- Probenacid
3. Physical Therapy
Day Care
1. Injectable medications
2. Intra articular Steroid Injection
Referral criteria:
not applicable
WHO DOES WHAT? And TIMELINES
Doctor
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Counsel the patient for prevention and dietary advice.
Nurse
counseling the patient. Injectable treatment
Technician
Appropriate bracing
Physiotherapy
Resources Required For One Patient / Procedure (Patient Weight 60 Kgs)
(Units to be specified for human resources, investigations, drugs and consumables and equipment. Quantity to also be specified)
| Situation | Human Resources | Investigations | Drugs & Consumables | Equipment |
| 1. | Doctor Nurse Technician | 1. X Ray 2. MSU crystals in Synovial fluid and tophi 3. Serum Uric Acid Level 4. Complete Blood Picture 5. ESR 6. CRP 7. Renal function test | e. NSAIDs f. Colchicine g. Steroid h. Uric acid lowering agents i. Consumables for surgery | Lab equipment Imaging equipment Exercise equipments Equipments for Operating Room |
| 2. (In Addition to Situation 1) |

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd