- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
Unique retinal scar visible in Ebola Survivors
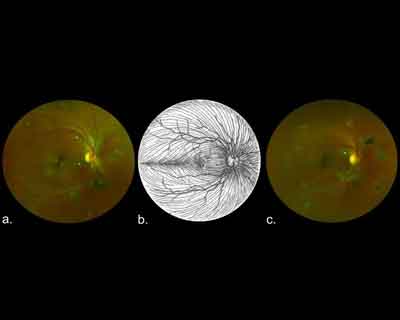
Researchers from the University of Liverpool have conducted a study of Ebola survivors to determine if the virus has any specific effects on the back on the eye using an ultra widefield retinal camera.
To find out more about the broad-ranging symptoms of Post Ebola Syndrome (PES), a clinical research team led by Dr Janet Scott and Dr Calum Semple, from the University's Institute of Translational Medicine, assessed survivors discharged from the Ebola Treatment Unit at the 34th Regiment Military Hospital in Freetown, Sierra Leone.
Two years on from the Ebola outbreak in West Africa, and many Ebola survivors are still presenting with symptoms of post-Ebola syndrome (PES), including joint and muscle pains and psychiatric and neurological problems.
Hiding viruses
Viruses, like Ebola, can stay hidden in our bodies by exploiting a vulnerability in our immune systems. This vulnerability is called "immune privilege," and comes from an old observation that foreign tissue transplanted into certain parts of the body don't elicit the usual immune response. This includes the brain, spinal cord, and eyes. Scientists believe this is because the brain, spinal cord, and eyes are simply too delicate and important to withstand the inflammation that's typical of an immune response.
An eye team led by Dr Paul Steptoe, compared eye examinations of PES sufferers in Sierra Leone and the control population. A total of 82 Ebola survivors who had previously reported ocular symptoms and 105 unaffected controls from civilian and military personnel underwent ophthalmic examination, including widefield retinal imaging.
The results of the research, which has been published in the Emerging Infectious Diseases journal, shows that around 15% of Ebola survivors examined have a retinal scar that appears specific to the disease.
Reduced vision
Dr Steptoe, said: "The distribution of these retinal scars or lesions provides the first observational evidence that the virus enters the eye via the optic nerve to reach the retina in a similar way to West Nile Virus. Luckily, they appear to spare the central part of the eye so vision is preserved. Follow up studies are ongoing to assess for any potential recurrence of Ebola eye disease.
"Our study also provides preliminary evidence that in survivors with cataracts causing reduced vision but without evident active eye inflammation (uveitis), aqueous fluid analysis does not contain Ebola virus therefore enabling access to cataract surgery for survivors."
For more details click on the link : Paul J. Steptoe, Janet T. Scott, Julia M. Baxter, Craig K. Parkes, Rahul Dwivedi, Gabriela Czanner, Matthew J. Vandy, Fayiah Momorie, Alimamy D. Fornah, Patrick Komba, Jade Richards, Foday Sahr, Nicholas A.V. Beare, Malcolm G. Semple. Novel Retinal Lesion in Ebola Survivors, Sierra Leone, 2016. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 2017; 23 (7) DOI: 10.3201/eid2307.161608
To find out more about the broad-ranging symptoms of Post Ebola Syndrome (PES), a clinical research team led by Dr Janet Scott and Dr Calum Semple, from the University's Institute of Translational Medicine, assessed survivors discharged from the Ebola Treatment Unit at the 34th Regiment Military Hospital in Freetown, Sierra Leone.
Two years on from the Ebola outbreak in West Africa, and many Ebola survivors are still presenting with symptoms of post-Ebola syndrome (PES), including joint and muscle pains and psychiatric and neurological problems.
Hiding viruses
Viruses, like Ebola, can stay hidden in our bodies by exploiting a vulnerability in our immune systems. This vulnerability is called "immune privilege," and comes from an old observation that foreign tissue transplanted into certain parts of the body don't elicit the usual immune response. This includes the brain, spinal cord, and eyes. Scientists believe this is because the brain, spinal cord, and eyes are simply too delicate and important to withstand the inflammation that's typical of an immune response.
An eye team led by Dr Paul Steptoe, compared eye examinations of PES sufferers in Sierra Leone and the control population. A total of 82 Ebola survivors who had previously reported ocular symptoms and 105 unaffected controls from civilian and military personnel underwent ophthalmic examination, including widefield retinal imaging.
The results of the research, which has been published in the Emerging Infectious Diseases journal, shows that around 15% of Ebola survivors examined have a retinal scar that appears specific to the disease.
Reduced vision
Dr Steptoe, said: "The distribution of these retinal scars or lesions provides the first observational evidence that the virus enters the eye via the optic nerve to reach the retina in a similar way to West Nile Virus. Luckily, they appear to spare the central part of the eye so vision is preserved. Follow up studies are ongoing to assess for any potential recurrence of Ebola eye disease.
"Our study also provides preliminary evidence that in survivors with cataracts causing reduced vision but without evident active eye inflammation (uveitis), aqueous fluid analysis does not contain Ebola virus therefore enabling access to cataract surgery for survivors."
For more details click on the link : Paul J. Steptoe, Janet T. Scott, Julia M. Baxter, Craig K. Parkes, Rahul Dwivedi, Gabriela Czanner, Matthew J. Vandy, Fayiah Momorie, Alimamy D. Fornah, Patrick Komba, Jade Richards, Foday Sahr, Nicholas A.V. Beare, Malcolm G. Semple. Novel Retinal Lesion in Ebola Survivors, Sierra Leone, 2016. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 2017; 23 (7) DOI: 10.3201/eid2307.161608
Dr Calum SempleDr SteptoeEbolaEbola survivorsPESPost Ebola SyndromeRegiment Military HospitalRetinaSierra LeoneVirus
Next Story
NO DATA FOUND

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd