- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
Diffusion MRI findings of transient global amnesia
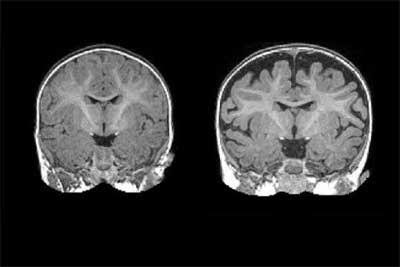
Transient global amnesia (TGA) is a reversible, benign, mostly nonrecurrent clinical syndrome of anterograde amnesia lasting up to 24 hours, manifesting as repetitive questioning and occasionally retrograde amnesia, without any gross neurological deficit.
Tarun P. Jain, a radiologist at Universal Medical Imaging, Canberra, Australia, and colleagues, conducted a study to describe the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings in patients with TGA, specifically on Diffusion Weighted Imaging (DWI) sequence.
The study was published in the Indian Journal of Radiology and Imaging.
DWI is a form of MRI which is based upon the measurement of random Brownian motion of water molecules within a voxel of tissue resulting in the generation of contrast in MR images.
For the study, the researchers retrospectively analyzed MRI findings in 12 patients (7 female and 5 male) with a clinical diagnosis of TGA. The mean age of the patients was 65.67 years (range 61-74 years). MRI brain was performed with a 3T scanner on 11 patients and 1.5T scanner on 1 patient. DWI was acquired at B value of 1000 s/mm2 in 4 patients, 2000 s/mm2 in 2 patients and both 1000 and 2000 s/mm2 in 6 patients.
Key Findings:
- 11 of the 12 patients showed punctate foci of restricted diffusion in hippocampus (mean size 3.7 mm (range 2-6.5 mm).
- 10 patients showed foci in left hippocampus.
- Nine patients showed a single focus, 1 patient showed three foci and 1 patient showed four foci.
- In 6 patients who had DWI MRI at both B values, scans at B value of 1000 s/mm2 revealed an abnormality in 4 patients, while higher B value imaging improved sensitivity in one patient and one patient had a negative scan at both B values.
"We have highlighted the MRI finding of typical punctate foci of a bright signal in hippocampus seen on DWI in patients diagnosed with TGA. Detection on a routine stroke MRI protocol can avoid the need for dedicated TGA protocols or repeat scan, improving the workflow," concluded the authors.
Jain TP, Patel R, Gawarikar Y. Transient global amnesia: Diffusion MRI findings. Indian J Radiol Imaging [serial online] 2018 [cited 2018 Jun 2];28:6-9. Available from: http://www.ijri.org/text.asp?2018/28/1/6/228686

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd