- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
Diffuse disease, tandem lesions (FFR/iFR) -Dr Prashant Jagtap
Fractional flow reserve (FFR) has become an invasive gold standard for lesion assessment in the catheterization laboratory.As iFR is calculated and recorded during the resting state without the need to induce hyperemia,this technology differs from FFR in various aspects. In the recent two large randomized control trials: DEFINE-FLAIR and iFR-SWEDEHEART, iFR guided PCI was demonstrated to be non-inferior to FFR guided PCI.
While assessing serial (tandem) lesions by FFR, the following practical steps are recommended:
- Pass the pressure wire beyond the last lesion and measure FFR(total) across all the lesions with IV adenosine.
- If total FFR in step 1 is <0.80, then perform a pressure pullback during IV adenosine hyperemia.
- Determine which of the lesions produces the biggest pressure gradient(ΔP),treat it first.
- Stent the lesions with the largest gradient (ΔP)- ideally≥10 mmHg.
- Re-assess the remaining lesions, repeating the standard FFR procedure, if FFR <0.80, stent the next lesion.
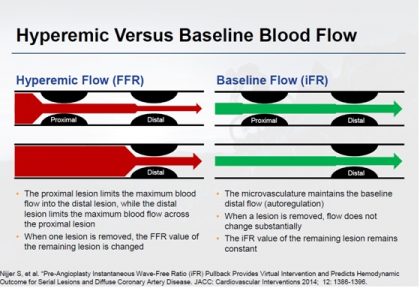
Occasionally, the pressure wire pullback may demonstrate diffuse graded step-ups in pressure gradient along the length of the artery.This indicates diffuse disease.
iFR pullback assessments map the ischaemic contribution of each lesion without the confounding effect observed with FFR pullback assessment. Calculating the individual drops in iFR or looking for the largest step up,the lesion having the largest impact on iFR value can be determined.
Following are the procedural tips to assess the significance of tandem lesions:
- Pullback the guide wire slowly and steadily.
- Do not interrupt the pullback or advance the wire distally while making the pullback measurement.
- Always view the entire iFR pullback recording and use the same iFR pullback range for comparing runs in the same vessel.
- While repeating a pullback in the same vessel, start from the same distal location.
- iFR scout may be useful for assessing serial lesions and diffuse disease as well as for documenting treatment results, without the need for a hyperemic agent.
- Consider the Hybrid approach if the distal iFR value falls within the FFR zone.

Despite the non-inferiority of iFR in short term clinical outcomes, when compared to FFR,there in currently insufficient data regarding the long term prognosis in iFR- guided revascularisation.Long term outcomes beyond 12 months will determine whether iFR may replace FFR as a technique of choice to assess lesion specific ischemia-guided revascularization.For complex anatomy,including serial or diffuse disease assessment,the iFR technique appears to be particularly helpful for pullback measurements as well as rapid multivessel stenting.
The author, Dr Prashant Jagtap is a Sr. Interventional Cardiologist & Clinical Advisor at Wockhardt Heart Hospital, Nagpur. He is presenting on the topic Diffuse disease, tandem lesions (FFR/iFR) at India live 2018.

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd