- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
Diagnosis and Treatment of Pediatric Solid Tumors-Standard Treatment Guidelines
Pediatric solid tumours are a very diverse group of diseases with differing biologies and behaviours and a substantial proportion consists of characteristic entities that are rarely seen in adults.
Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India has issued the Standard Treatment Guidelines for Pediatric Solid Tumors.
Following are the major recommendations :
Case definition
The International Classification of Childhood Cancer, Third Edition (ICCC-3) contains 12 main diagnostic groups:
I. Leukemias, myeloproliferative diseases, and myelodysplastic diseases
II. Lymphomas and reticuloendothelial neoplasms
III. CNS and miscellaneous intracranial and intraspinal neoplasms
IV. Neuroblastoma and other peripheral nervous cell tumors
V. Retinoblastoma
VI. Renal tumors
VII. Hepatic tumors
VIII. Malignant bone tumors
IX. Soft tissue and other extraosseous sarcomas
X. Germ cell tumors, trophoblastic tumors and neoplasms of gonads
XI. Other malignant epithelial neoplasms and malignant melanomas
XII. Other and unspecified malignant neoplasms
All of the groups except retinoblastoma are split into subgroups, and the most heterogeneous subgroups are in turn split into divisions.
The pediatric solid tumors comprise of group III to XII. Group III and VIII requiring specialized orthopedic and neuro-surgery and neuro-radiation expertise are considered separately.
INCIDENCE OF THE CONDITION IN OUR COUNTRY
The annual incidence of cancer in children under 15 years of age is between 38 and 124 per million. There is no organized Paediatric solid tumours registry in India; hence, robust epidemiologic data is not available for the country. All currently quoted data is based on population-based cancer registries across India under the National Cancer Registry Program.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
- Trauma
- Infection
- Benign tumor
PREVENTION AND COUNSELING
The occurrence and progression of paediatric solid tumours like most other tumors is influenced by a variety of genetic changes. The accumulation of changes varies between tumor types and the exact pattern varies even for a particular tumor type. Genetic counseling is the communication of information and advice about inherited conditions. A standard medical history and examination is required for the affected person and in addition the family pedigree needs to be constructed. For certain tumor syndromes it might also be necessary to examine apparently normal parents and other relatives for minor features of the condition. Alternatively, if a specific mutation is identified in the proband, genetic testing for this mutation can subsequently be offered to the relatives where appropriate. Counseling needs to include all aspects of the condition and the depth of explanation should be matched to the educational background of the couple. Parents may feel responsible for the condition of their child. These fears need to be aired and allayed. In inherited tumors and syndromes there is an additional need to minimize feelings of guilt and stigmatization.
OPTIMAL DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA, INVESTIGATIONS, TREATMENT & REFERRAL CRITERIA
Situation 1: At Secondary Hospital/ Non-Metro situation: Optimal Standards of Treatment in Situations where technology and resources are limited
Clinical Diagnosis
History & Clinical Examination
Documentation of congenital anomalies, evident signs of clinical syndromes Assessment of Performance Status and Nutrition
Baseline investigations
| Complete Haemogram | Hemoglobin, RBC, WBC, Platelets, ESR, Coagulation Profile |
| Routine Biochemistry | FBS, RFT, LFT & LDH |
| Serology | HbsAg, HCV, HIV |
Histological Examination: (Immunohistochemistry)
| Tissue diagnosis | FNAC, Biopsies, Cytology, bone marrow studies |
Diagnostic Imaging: Contemporary imaging modalities
| Radiology | X-ray, USG, CT scan |
Treatment
Standard Operating procedure
In Patient:
- All sick pediatric solid tumor patients are admitted for supportive care and initiation of treatment as required.
- Patients planned for elective surgery are admitted a day prior to the surgery with complete work-up and treatment plan.
- Patients with fever are admitted for management of Febrile Neutropenia. Once their
condition is stable they are discharged and followed up in the OPD.
Out Patient:
- Patients undergo complete clinical evaluation and are recommended investigations to confirm the diagnosis and complete staging.
- Sick patients and those with Medical oncologic emergencies are admitted in the ward for emergency management.
- Stable patients are followed up in the OPD till the diagnosis and staging workup is complete.
- Treatment decisions are taken in the Multidisciplinary Joint clinics at diagnosis, at the time of local therapy planning, at time of completion of treatment and if required anytime in between.
Day Care
- Treatment for all stable pediatric solid tumor patients is started in the OPD/Day care. Admission is limited to patients with uncontrolled co-morbid conditions or complications of the disease or treatment related complications.
- Patients with advanced/relapsed disease not amenable to treatment are considered for palliative care and referred for the same.
Referral criteria:
Situation 2: At Super Specialty Facility in Metro location where higher-end technology is available
Clinical Diagnosis
History & Clinical Examination
Documentation of congenital anomalies, evident signs of clinical syndromes
Assessment of Performance Status and Nutrition
Investigations
Baseline investigations
| Complete Haemogram | Hemoglobin, RBC, WBC, Platelets, ESR, Coagulation Profile |
| Routine Biochemistry | FBS, RFT, LFT & LDH |
| Serology | HbsAg, HCV, HIV |
Histological Examination: (Immunohistochemistry)
| Tissue diagnosis | FNAC, Biopsies, Cytology, bone marrow studies |
| Molecular pathology | EWS-FLI 1, EWS-WT1, SYT-SSX1, n-myc, PAX-3FKHR etc |
| Tumor Markers | AFP, BHCG, Urinary VMA, HVA |
Diagnostic Imaging: Contemporary imaging modalities
| Radiology | X-ray, USG, CT scan, MRI |
| Nuclear imaging | PET scan, Bone scan, MIBG scan |
Treatment:
Standard Operating procedure
In Patient
- All sick pediatric solid tumor patients are admitted for supportive care and initiation of treatment as required.
- Patients planned for elective surgery are admitted a day prior to the surgery with complete work-up and treatment plan.
- Patients with fever are admitted for management of Febrile Neutropenia. Once their condition is stable they are discharged and followed up in the OPD.
Out Patient
- Patients undergo complete clinical evaluation and are recommended investigations to confirm the diagnosis and complete staging.
- Sick patients and those with Medical oncologic emergencies are admitted in the ward for emergency management.
- Stable patients are followed up in the OPD till the diagnosis and staging workup is complete.
- Treatment decisions are taken in the Multidisciplinary Joint clinics at diagnosis, at the time of local therapy planning, at time of completion of treatment and if required anytime in between.
Day Care
- Treatment for all stable pediatric solid tumor patients is started in the OPD/Day care. Admission is limited to patients with uncontrolled co-morbid conditions or complications of the disease or treatment related complications.
- Patients with advanced/relapsed disease not amenable to treatment are considered for palliative care and referred for the same.
Referral criteria:
- Patients with logistic problems will receive referral letters for institutions with adequate infrastructure and expertise including the necessary protocols.
- Patients with advanced incurable disease will be triaged and will undergo counseling by the DMG's palliative care team. Appropriate instruction and arrangement will be provided for referral of these patients for supportive care to institutions at convenient distance from their hometowns.
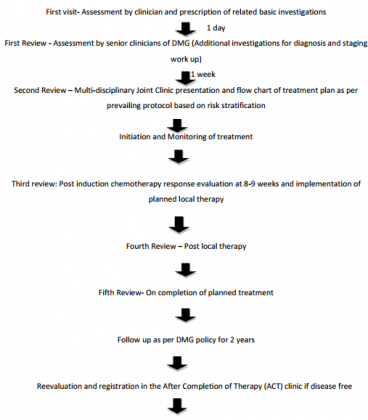
Follow up in ACT clinic annually to monitor growth and development, late effects and encourage survivorship programme – "UGAM
RESOURCES REQUIRED FOR ONE PATIENT / PROCEDURE (PATIENT WEIGHT 60 KGS)
(Units to be specified for human resources, investigations, drugs and consumables and equipment. Quantity to also be specified)
| HUMAN RESOURCES | INVESTIGATIONS | DRUGS | EQUIPMENT |
| 1. Qualified Surgeon 2. Qualified Radiation Oncologist 3. Qualified Pediatric Medical Oncologist 4. Pathologist 5. Radiologist 6. Trained Nurses 7. General Physician 8. Palliative Care specialist 9. Anesthetist 10. Clinical Psychologist 11. Medical Social Worker | Haematological, Biopsy, Histopathology, CT Scan/MRI, Molecular (IHC) analysis. | NSAIDs, Opioids Antacids, Antiemetics, Contrast medium Chemotherapeutics ( Most commonly used drugs) Vincristine, Ifosphamide, Doxorubicin, Cisplatin, Carboplatin, Etoposide, Cyclophosphamide, Actinomycin D, Bleomycin, Topotecan, Methotrexate, Temozolamide, 13 cis-Retinoic acid, 5FU,Vinblastine | OT equipment, Electrical cautery, Hormonic scalpel, Intaoperative Xray unit, Anesthesia trolley, mechanical ventilators, Suction apparatus, nebulizers, Co60 unit, Linear Accelerator, 2D/3D Simulators, Treatment planning system, |
Guidelines by The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare :
Dr Anil K. D' Cruz
Director and
Chief Head and Neck Services,
Tata Memorial Hospital, Mumbai

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd