- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
Deviated Nasal Septum : Standard Treatment Guidelines
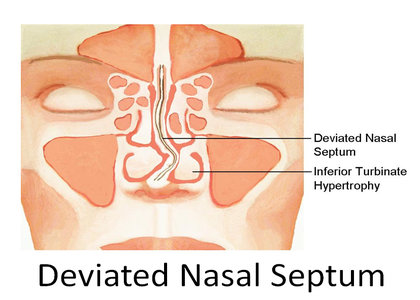
Deviated Nasal Septum (DNS) is the deflection of nasal septum from midline and it may be caused by birth trauma, trauma to face during life or due to asymmetric growth of cartilages and bones of nose. It may present with nose block, recurrent nasal discharge, infections of nose and sinuses, bleeding from nose or headaches. In gross DNS, there may be a concomitant deviation of external nose also.
Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India has issued the Standard Treatment Guidelines for Deviated Nasal Septum (DNS). Following are the major recommendations:
Incidence In Our Country
Very few people have absolutely straight nasal septum. Most minor DNS are not symptomatic and do not require treatment. Only symptomatic DNS need be mentioned to the patient and treated.
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis includes:
1. Acute or chronic Rhinosinusitis
2. Nasal Allergy
3. Large Adenoid mass in children
4. Foreign Body/ Rhinolith in children
5. Nasal Polyps
6. Growths/ Tumors of nose
Prevention And Counselling
DNS cannot be prevented. Minor deviations do not require treatment. Symptomatic DNS can be corrected by surgery through the nostrils under Local or General Anaesthesia. Surgery is usually done after the age of 16 years when the facial growth is complete. Surgery in younger patients may be undertaken if grossly symptomatic and not amenable to medical management for nasal obstruction.
In septoplasty, the deviated portion of the nasal septum is removed. The nose is packed for 1 -2 days to prevent bleeding. Patient is discharged after removal of packs. The nose takes 1 -2 weeks to heal completely.
Optimal Diagnostic Criteria, Investigations, Treatment & Referral Criteria
At Secondary Hospital/ Non Metro Situation
Clinical Diagnosis :
The diagnosis of DNS is made on:
1. History of facial trauma if any
2. Complaints of nasal obstruction, discharge, bleeding or headache
3. Complete ENT examination
4. Nasal examination including anterior rhinoscopy and Cold Spatula Test.
5. Evaluation of extent and site of trauma to face if any
Investigations :
1. complete blood count,
2. bleeding and clotting time.
3. X Ray of paranasal sinuses
4. X Ray of nasal bones in trauma.
5. Other investigations based on general clinical condition
Treatment :
Out Patient : Associated conditions causing nasal obstruction can be treated medically as out patient with:
1. Antihistaminics oral or nasal sprays
2. Monteleukast
3. Steroid nasal sprays
4. Antibiotics for nasal and sinus infections
Day Care :
1. Removal of foreign body or rhinolith from nose.
2. Anterior nasal packing for bleeding from nose.
3. Septoplasty surgery may be performed as day care if adequate facility for post op care is available at home.
Inpatient :
1. Septoplasty.
2. Manangement of comorbities.
Referral Criteria :
1. External deformity requiring rhinoplasty
2. Nasal Polyps requiring endoscopic sinus surgery
3. Bleeding not controlled with anterior and posterior nasal packing.
4. Midface fractures would require a maxillofacial consultation.
5. Other co morbidities requiring appropriate cross consultations.
At Tertiary Hospital/ Metro Situation
Clinical Diagnosis :
The evaluation should include:
1. Review of general evaluation of clinical condition
2. Complete ENT examination
3. Nasal Endoscopic examination under Local/ General Anaesthesia to identify deviation of septum, sinusitis, polyps, site of bleeding or any growths in nose.
4. Evaluation of extent and site of trauma to face if any
Investigations :
1. complete blood count,
2. bleeding and clotting time.
3. Prothrombin Time/ PTTK/ INR
4. CT Scan of nose and paranasal sinuses
Treatment :
Additional measures which may be required are
Out Patient / Day Care : Endoscopic electro cautery of bleeding point
Inpatient :
1. Rhinoplasty for external deviation of nose
2. Endoscopic sinus surgery
3. Maxillofacial reduction of fracture and wire and plate fixation.
4. Biopsy and / or excision of tumor if any
5. Management of comorbidiites.
Referral Criteria :
In adequate facilities for any of the above.
Guidelines by The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare :
Dr J M Hans Ex-HOD Dept. of Otorhinolaryngology Dr.RML Hospital New Delhi

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd