- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
CT Combined with angiography effective for diagnosing insulinomas
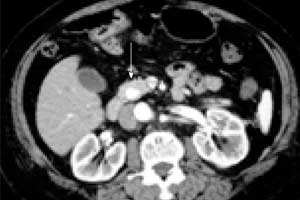
Computed tomography (CT) during celiac artery angiography is a sensitive diagnostic procedure for localizing insulinomas, according to a new study published in the journal Cancer Imaging. The results demonstrate that CT combined with angiography, can prioritize the pancreatic region for exploration and guide a pancreatic resection.
Insulinomas are the most common cause of hypoglycemia resulting from endogenous hyperinsulinism. Approximately 90-95% of insulinomas are benign, and long-term cure with a total resolution of preoperative symptoms is expected after complete resection.
Feng Duan, Department of Interventional Radiology, the General Hospital of Chinese People’s Liberation Army, Beijing, China, and colleagues conducted the study to assess the performance of CT during celiac artery angiography for preoperative localization of clinically suspected small insulinomas (< 2 cm in diameter).
Insulinomas are classified as neuroendocrine tumors derived from beta cells in the pancreas, which secrete insulin. Most insulinomas are functional, with typical symptoms according to the Whipple triad. Although clinical symptoms are evident, insulinomas are often small, with more than 80% of the insulinomas smaller than 2 cm in diameter. In this group of patients, 92.9% of the insulinomas are < 2 cm. Because of their small size, they are likely to be missed during conventional imaging exams. For improving the cure rate, identification of location and number of insulinomas before an operation is very important.
Read Also: Diagnosis and management of Pancreatic Carcinoma – New Standard Treatment Guidelines
From January 2013 to November 2016, 42 patients with hypoglycemic symptoms underwent celiac artery angiography, superior mesenteric artery angiography and CT during celiac artery angiography by a combined CT/digital subtraction angiography system, MIYABI Angio CT plus an Artiszeeceiling (SIEMENS, Germany). The patient group consisted of 13 males and 29 females, age 17–69 years (average, 45.4 ± 13.5 y). After diagnosis, all 42 patients were operated. Obtained images were retrospectively analyzed and compared with findings from post-operation pathology.
All interventional radiology procedures were performed successfully with no complications. The sensitivity of angiography alone for insulinoma was 76.1% (32/42), at combined CT/digital subtraction angiography, 4 more nodules were found (sensitivity, 85.7%, 36/42), while 6 false-negatives were observed (all false-negative lesions were less than 2 cm). A total of 64 ml to 80 ml contrast media was used per patient.
Advantages of the combination of angiography with CT during celiac artery angiography:
- It can provide greater enhancement of pancreatic tumors by the administration of contrast material directly into the proper artery.
- CT provides significantly higher spatial resolution than DSA, thus it provides a more precise diagnosis for small lesions, especially lesions, which overlay with duodenum or spleen.
- Only local injection of contrast medium is required, so the dosage of contrast medium is greatly reduced compared to conventional CT. In the study, the dose of contrast medium for CT was 12 ml, and even with the addition of contrast medium for angiography, the total dose of contrast media was still lower than applied with a conventional CT.
- Two exams can be performed simultaneously, and through the integration of the two exam findings, small insulinomas can more precisely be located.

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd