- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
Carbetocin more effective than Oxytocin in PPH prevention
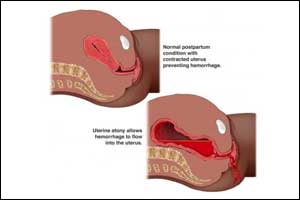
Postpartum haemorrhage (PPH), is the leading cause of maternal mortality worldwide which can pose a serious risk to the health and life of mothers. For reduction of excessive bleeding at childbirth, the routine administration of a uterotonic drug called Oxytocin which contracts the uterus has become a standard practice across the world.
However, a study published in Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews suggests that alternative drugs-- ergometrine plus oxytocin; misoprostol plus oxytocin; and carbetocin on its own, are more effective than the standard drug (oxytocin) currently used to stop postpartum haemorrhage.
The study was conducted by Ioannis Gallos, clinician scientist at University of Birmingham, and colleagues, with an objective to identify the most effective uterotonics (among oxytocin, misoprostol, ergometrine, carbetocin or combinations of these) for PPH prevention, and generate a ranking according to their effectiveness and side-effect profile.
In this study, researchers from the Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group have reviewed the data of the births of 88,000 women who took part in 140 randomised trials.
All the available evidence were analysed for comparison of the drugs followed by calculation of ranking among them, providing robust effectiveness and side-effect profiles for each drug. Side-effects can include vomiting, high blood pressure and fever.
Dr Gallos said, "Whilst death from postpartum haemorrhage is a rare complication, it is the most common reason why mothers die in childbirth worldwide and happens because a woman's womb has not contracted strongly enough after birth and results in excessive bleeding.
"Currently, to reduce excessive bleeding at childbirth, the standard practice across the world is to administer to women after childbirth a drug called oxytocin - a uterotonic which contracts the uterus and stimulates contractions to help push out the placenta.
"Our research has highlighted which drugs may be more effective than oxytocin and we hope that this could impact existing recommendations and save mothers lives worldwide."This Cochrane review is expected to be updated later this year to incorporate the results of some key ongoing studies which will report their findings in coming months, including a large study involving around 30,000 women across 10 different countries comparing the effectiveness of carbetocin versus oxytocin for preventing bleeding in women having a vaginal birth, and a UK-based trial involving more than 6,000 women comparing carbetocin, oxytocin and ergometrine plus oxytocin combination."
For more information click on the link: 10.1002/14651858.CD011689.pub2
bleeding after childbirthCarbetocinCochrane Database of Systematic ReviewsDr. Ioannis Gallosdrug for reduction of maternal mortalityergometrineIoannis GallosMaternal mortalitymisoprostolOxytocinPostpartum haemorrhagePPHprevention of bleeding in women after childbirth
Source : With inputs from Cochrane Database of Systematic ReviewsNext Story
NO DATA FOUND

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd