- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
Breakthrough: Scientist develop battery-free medical implants powered by body fluids
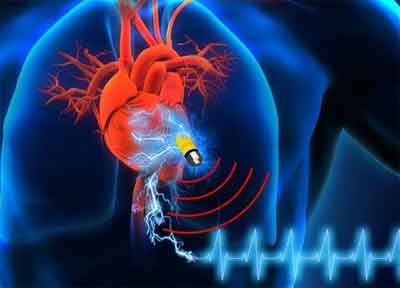
Scientists have developed a new energy storage device which operates using fluids in the human body, and could lead to longer-lasting, battery-free pacemakers and other implantable medical devices.
The bio-friendly energy storage system called biological super-capacitor is powered by charged particles, or ions, from the body's fluids like blood serum and urine.
Pacemakers - which help regulate abnormal heart rhythms - and other implantable devices have saved countless lives.
However, they are powered by traditional batteries that eventually run out of power and must be replaced, meaning another painful surgery and the accompanying risk of infection.
In addition, batteries contain toxic materials that could endanger the patient if they leak.
Now, researchers from University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) and the University of Connecticut in the US propose storing energy in those devices without a battery.
The super-capacitor they invented charges using electrolytes from biological fluids like blood serum and urine, and it would work with another device called an energy harvester.
It converts heat and motion from the human body into electricity - in much the same way that self-winding watches are powered by the wearer's body movements.
That electricity is then captured by the super-capacitor.
"Combining energy harvesters with super-capacitors can provide endless power for lifelong implantable devices that may never need to be replaced," said Maher El-Kady, a UCLA postdoctoral researcher.
Modern pacemakers are typically about 6 to 8 millimetres thick, and about the same diameter as a 50-cent coin; about half of that space is usually occupied by the battery.
The new super-capacitor is only 1 micrometre thick - much smaller than the thickness of a human hair - meaning that it could improve implantable devices' energy efficiency.
It also can maintain its performance for a long time, bend and twist inside the body without any mechanical damage, and store more charge than the energy lithium film batteries of comparable size that are currently used in pacemakers.
The new biosupercapacitor comprises a carbon nanomaterial called graphene layered with modified human proteins as an electrode, a conductor through which electricity from the energy harvester can enter or leave.
The new platform could eventually also be used to develop next-generation implantable devices to speed up bone growth, promote healing or stimulate the brain, said Richard Kane from UCLA, who led the study published in the journal Advanced Energy Materials.

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd