- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
Birch pollens trigger late Skin reactions in patients with atopic dermatitis
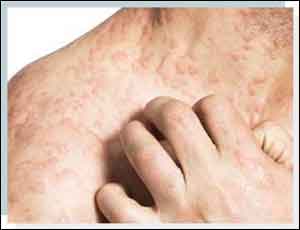
About 35% patients with atopic dermatitis developed allergic skin reactions with birch pollen‐related foods. Atopic dermatitis (eczema) is a condition that makes your skin red and itchy.
Atopic dermatitis is common in children but can occur at any age. It is a chronic disease which tends to flare periodically. It may be accompanied by asthma or hay fever. The fruits and vegetables most commonly related to birch tree are apples, peaches, prunes, pears, cherries, apricots, carrots, celery, almonds, hazelnuts, and peanuts.
Anja Wassmann-Otto et.al conducted a retrospective study to determine how frequently birch pollen‐related foods induce a deterioration of eczema and also to evaluate the diagnostic value of specific IgE (sIgE).
A total of 182 children and adults with AD and suspected birch pollen‐related food allergy were included in the study who had to undergo 261 double‐blind placebo‐controlled food challenges (DBPCFC). Total and specific IgE levels were determined prior to DBPCFC.
Key results of the study:
- 65 patients developed allergic reactions (responders) upon DBPCFC with birch pollen‐related foods (n=103 DBPCFC).
- Of these, 32 patients exhibited significant deterioration of AD defined as a median increase of 15.4 SCORAD index points (95% CI 12.4‐16.3) from baseline making up 37% of all positive reactions.
- Responders showed significantly higher sIgE levels to birch pollen and apple as well as a higher prevalence of allergic rhinoconjunctivitis compared to non‐responders (P<.05).
- However, patients with late eczematous response could not be differentiated from those with isolated immediate-type reactions by specific IgE levels
The study concluded that patients with AD sensitive to birch pollen, related foods can aggravate eczema. Sufficient markers for prediction of late eczematous reactions are still not available, DBPCFC cannot be replaced in the diagnosis of birch pollen‐related foods in patients with the AD.
For more reference log on to: http://10.1111/all.13454

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd