- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
Bedside eye ultrasound quick method to diagnose raised intracranial pressure
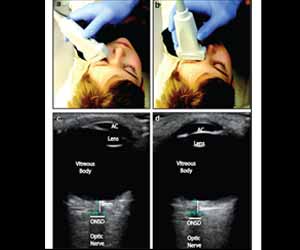
Bedside ultrasonography of the eye has many clinical applications, including the assessment for haemorrhage, foreign body, lens dislocation, retinal detachment, and of course optic nerve sheath diameter. Findings from a new systematic review and meta-analysis have revealed that bedside optic nerve ultrasound holds promise for diagnosing increased intracranial pressure in children and adults. It is a noninvasive, quick method for diagnosing increased intracranial pressure. The study has been published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Bedside optic nerve ultrasound is an easy-to-use test for diagnosing increased intracranial pressure . It involves applying a layer of gel to the closed eyelid with the patient in the supine position. Traditional diagnostic tests to diagnose increased intracranial pressure such as CT scan, lumbar puncture, and intracranial drains are limited by invasiveness, contraindications, radiation exposure, availability, and need for patient transportation.
Researchers from McMaster University analyzed 71 studies involving 4,551 patients to examine the accuracy of optic nerve ultrasound for diagnosing increased intracranial pressure. They found an excellent accuracy of optic nerve ultrasound in detecting increased intracranial pressure among children and adults, patients suffering from traumatic and non-traumatic causes of intracranial pressure (brain bleeds and tumours), and whether the specialist performing the ultrasound was a neurosurgeon, radiologist, emergency medicine clinician, neurologist, or critical care specialist. The authors recommend adding this useful tool in clinical practice to standard tests in diagnosing patients with suspected increased intracranial pressure.
The authors of an accompanying editorial suggest that these results should be considered with caution because the measurement of the optic nerve sheath diameter is riddled with greater challenges than other bedside ultrasonography clinical applications. They recommend future research to establish a standardized protocol for using optic nerve ultrasound and anticipate tele-ultrasound practice to be increasingly available.
Journal Information: Annals of Internal Medicine
For more details click on the link:
Abstract: http://annals.

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd