- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
Baby born with colon having appearnce of question-mark: NEJM case report
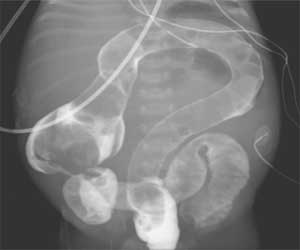
In a case report published in the journal NEJM (New England Journal of Medicine) describes the rare case of a baby born with a shortened colon that appeared in the shape of a question mark. Findings afterwards confirmed it to be a case of Hirschsprung’s disease -- a congenital absence of enteric ganglion cells resulting in a loss of bowel motility in affected areas.
The baby was born at 39 weeks of gestation to a 28-year-old woman. The patient experienced bilious emesis, failure in the passage of meconium, and abdominal distention within 24 hours after birth. Abdominal radiography revealed dilated bowel, a finding consistent with distal obstruction. A water-soluble contrast enema showed a uniformly distended and shortened colon that appeared in the shape of a question mark, a finding consistent with total colonic aganglionosis.
A specimen obtained at the bedside by transanal suction rectal biopsy had no ganglion cells found on hematoxylin and eosin staining, a negative result on calretinin staining, and abnormally thickened nerve fibres. These findings confirmed the diagnosis of Hirschsprung’s disease.
The patient was taken to the operating room, where laparoscopic serial frozen-section biopsy specimens of the entire colon were obtained and no ganglion cells were identified. Abundant ganglion cells were found at the level of the terminal ileum, and an end ileostomy was performed. Six months later, the patient underwent colectomy with stapled side-to-side anastomosis of the terminal ileum to the rectal remnant (Duhamel procedure). At the postoperative visit, the infant was having five to eight bowel movements daily and was growing well.
For more details click on the link: DOI: 10.1056/NEJMicm1811998

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd