- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
Artificial Intelligence can quickly and accurately report Chest X-Rays
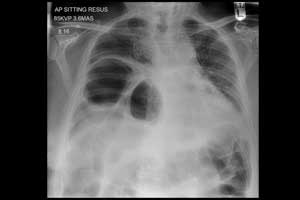
A new study has found that Artificial intelligence with deep learning algorithm trained on a large quantity of labelled data can accurately detect abnormalities on Chest x-ray. The latest study validates and tunes its deep learning system to detect chest x-ray abnormalities. The results have been published today in a research paper on Cornell University's online distribution system for research, arXiv.org. The paper is titled 'Can Artificial Intelligence Reliably Report Chest X-Rays?: Radiologist Validation of an Algorithm trained on 1.2 Million X-Rays'.
New clinically-validated, automated AI that can reliably separate normal from abnormal chest x-rays which are the most commonly performed, cost-effective diagnostic imaging tests ordered by physicians. This would be invaluable in addressing the problem of reporting backlogs and the lack of radiologists in the long run
Qure.ai's deep learning chest x-ray algorithms were tested on 1.2 million x-rays and their corresponding radiology reports to identify abnormal x-rays and other abnormalities such as blunted costophrenic angle, calcification, cardiomegaly, cavity, consolidation, fibrosis, hilar enlargement, opacity and pleural effusion. The system was tested against a 3-radiologist panel and set of 2,000 independent, de-identified and anonymized x-rays.
"The chest x-ray is a valuable health screening tool and a vital component of public health programs worldwide. The enormous volume produced each year creates an ever-increasing demand for radiologists," said Dr Shalini Govil, Quality Controller and Senior Advisor of the Columbia Asia Radiology Group. "Unfortunately, numerous chest x-rays displaying significant pathology are left neglected in piles of backlogs due to a lack of available radiologists to report them. Through semi-automation of the reporting process, AI can significantly reduce a radiologist's workload, improve report accuracy, reduce turnaround time and save lives."
"We used a triple blinded validation protocol to test the system on a set of 2,000 de-identified chest x-rays from the Columbia Asia Hospital archives. The study measured the performance of the algorithm against three independent opinions of practising radiologists," said Dr. Sundeep Reddivari, General Manager- Telemedicine, Columbia Asia Hospitals Pvt. Ltd. "The study found that a deep learning algorithm trained on a large number of labelled x-rays can independently, and most importantly, accurately detect abnormalities on chest x-rays."
"This study is a series of exciting firsts," said Prashant Warier, CEO & Co-founder Qure.ai. "This is the largest training dataset ever for a chest x-ray AI. It's also the largest validation study to date, measured against 2,000 x-rays - each read by three radiologists. And, finally, it's also the first paper to detect an 'abnormal' x-ray, consequently, our qXR algorithm is trained to differentiate between normal and abnormal x-rays."
Qure.ai's qXR detects 15 chest x-ray abnormalities at near-radiologist levels, with more than 90% accuracy. It also screens for tuberculosis and is used in public health screening programs around the world. qXR was trained with over one million curated X-rays and radiology reports, making it the most comprehensive and accurate chest X-ray detection algorithm available today.
"This is an exciting time for deep learning technologies in medicine," said Warier. "As these systems increase in accuracy, so will the viability of using deep learning to extend the reach of chest x-ray interpretation, improve reporting efficiency and save lives."
For further reference log on to : https://arxiv.org/abs/1807.07455

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd