- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
Around 5% increase in Type 1 diabetes among children: doctors
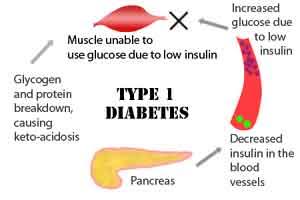
New Delhi : Cases of Type 1 diabetes among children have risen from one per cent to around five per cent in the last couple of years, doctors said on Sunday.
According to doctors more than 3,000 children are affected by type 1 diabetes, compared with about 600 around 20 years ago.
Doctors said that the prime reason behind the rise is the destruction of beta cells which produce insulin.
"Diabetes is occuring early because of increase in obesity in children, westernisation of diet, ingestion of high carbs and fat, lack of fruits and vegetables, and decrease in physical activity," said Meena Chhabra, a Delhi based diabeteologist.
Obesity has grown over 40 per cent among the children, Chhabra added.
Chabbra said that the symptoms include increased urination, increased hunger and thirst, frequent infections and loss of weight, extreme fatigue, and eventually drowsiness and coma, which is known as diabetic keto acidosis.
According to Ashraf Ghani, assistant professor of Endocrinology at AIIMS, currently 70,000 youngsters suffer from diabetes in India, which every year increases by 2-3 per cent.
"Childhood obesity is on the rise especially among the school children and may be feeding to this epidemic of diabetes," Ghani said.
"Diabetes in children is extremely dangerous, which the world is not realising. Type 1 diabetes was uncommon till now, but is increasing, and it may account for 2-3 per cent of total diabetes load," Ghani added.
The difference between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes is that the former usually starts in childhood or young adulthood while the latter is usually discovered in adulthood.

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd