- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
Anaphylaxis Management- Canadian 2018 Guidance
Anaphylaxis is an acute, potentially fatal systemic allergic reaction with varied mechanisms and clinical presentations. It is rapid in onset and potentially fatal with an estimated prevalence to be as high as 2 %. Clinical manifestations vary widely; however, the most common signs are cutaneous symptoms, including urticaria, angioedema, erythema and pruritus.
Key Messages are-
Anaphylaxis is the most severe form of an allergic reaction that is rapid in onset and potentially fatal.
Prompt recognition and treatment are critical in anaphylaxis.
The diagnosis is based primarily on clinical signs and symptoms.
The most common clinical manifestations are cutaneous symptoms, including urticaria and angioedema, erythema, and pruritus.
Referral to an allergist or immunologist should be considered for all persons who have experienced a previous anaphylactic episode.
Epinephrine is the drug of choice for anaphylaxis and should be given immediately, even if the diagnosis is uncertain; intramuscular administration into the anterolateral thigh is recommended.
There are no absolute contraindications to the use of epinephrine.
- Acute management may also involve oxygen therapy, intravenous fluids, and adjunctive therapies such as antihistamines or inhaled beta2-agonists.
Up to 15% of anaphylaxis cases will have a biphasic response, with the second wave of symptomatology.
The mainstays of long-term treatment include specialist assessment, avoidance measures, the provision of an epinephrine auto-injector and an individualized anaphylaxis action plan.
Causes of anaphylaxis
Most episodes of anaphylaxis are triggered through an immunologic mechanism involving immunoglobulin E (IgE) which leads to mast cell and basophil activation and the subsequent release of inflammatory mediators such as histamine, platelet activating factor, leukotrienes, tryptase and prostaglandins.
Common |
• Foods: most commonly peanuts, tree nuts, egg, fish, shellfish, cow's milk, and wheat |
• Medications: most commonly antibiotics and NSAID |
• Allergen immunotherapy |
• Insect stings (bees and wasps) |
• Unidentified (no cause found; idiopathic anaphylaxis) |
Less common |
• Exercise |
• Natural rubber latex |
• Semen |
• Hormonal changes: menstrual factors |
• Topical medications (e.g., chlorhexidine, polysporin) |
• Transfusions |
Signs and symptoms
Skin • Urticaria • Angioedema • Erythema (flushing) • Pruritus • Eczema Respiratory • Upper airway Nasal congestion Sneezing Hoarseness Cough Laryngeal edema • Lower airway Dyspnea Cough Bronchospasm Wheezing Chest tightness Cardiovascular • Hypotension • Dizziness • Syncope • Tachycardia | Gastrointestinal • Nausea • Vomiting • Abdominal pain • Diarrhea Neurologic • Lightheadedness • Dizziness • Confusion Oropharyngeal • Pruritus, tingling • Angioedema Other • Sense of impending doom • Anxiety |
Treatment-Treatment should be provided even if the diagnosis is uncertain since there is no contraindication to the use of epinephrine
Acute Management-
- The recommended dose of epinephrine for anaphylaxis is 0.01 mg/kg (maximum 0.5 mg) administered intramuscularly every 5–15 min as necessary.
- Intramuscular administration into the anterolateral thigh is recommended as it allows for more rapid absorption and higher plasma epinephrine levels compared to subcutaneous or intramuscular administration in the upper arm.
- Glucagon should also be considered in patients using beta-blockers.
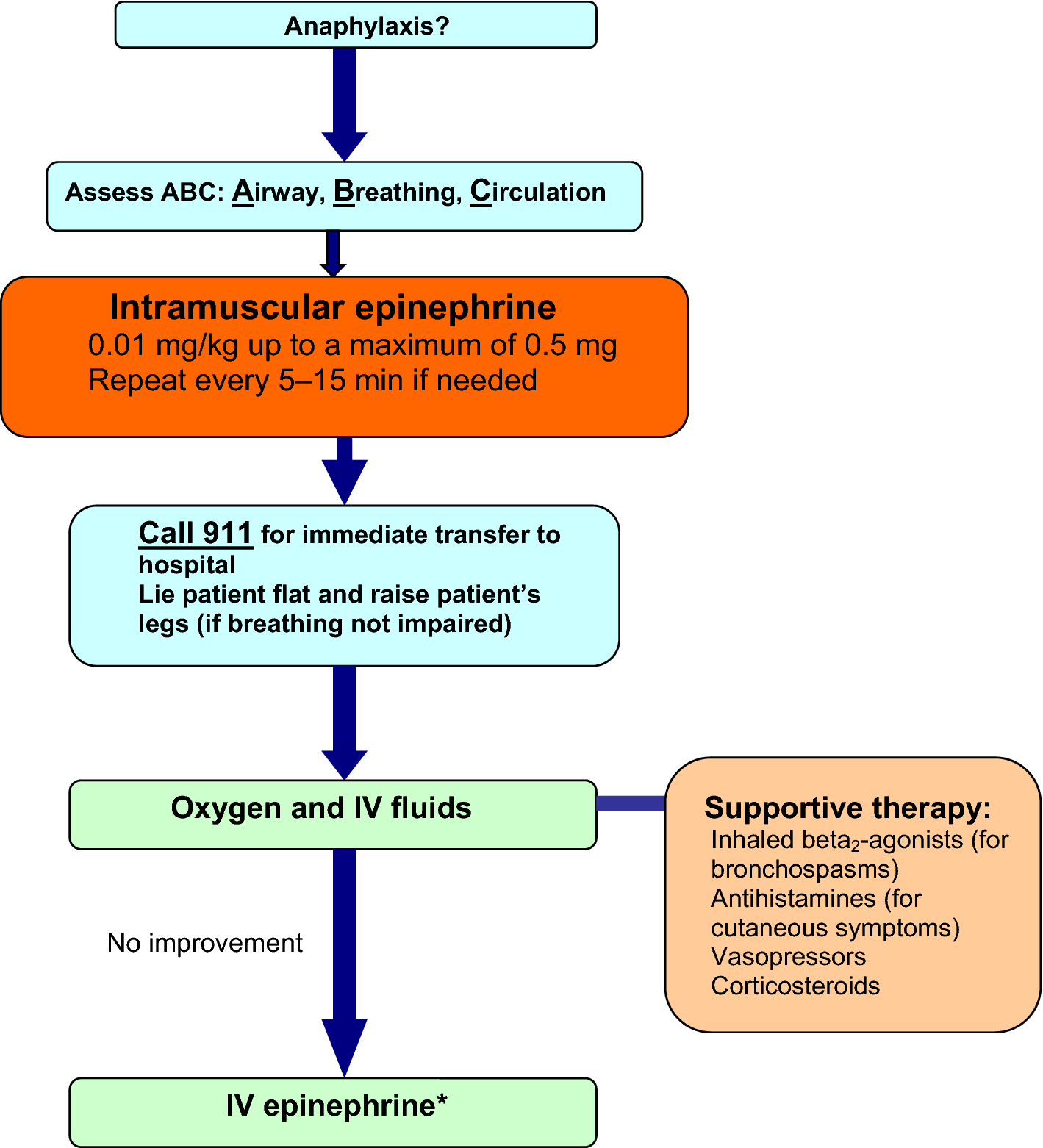
Long-term management
The mainstays of long-term management for patients who have experienced anaphylaxis include specialist assessment, a prescription for an epinephrine auto-injector, patient and caregiver education on avoidance measures, and the provision of an individualized anaphylaxis action plan.
Anaphylaxis action plan
Components of an anaphylaxis action plan
Contact details • Names and contact details for emergencies, including family members, allergist/immunologist and family doctor • Contact details for local emergency or ambulance services |
Allergens/triggers • Clear identification of allergens/triggers to be avoided – Include generic and proprietary names of drugs and possible cross-sensitivities, if relevant |
How to recognize the signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis • Mouth: itching, swelling of lips/tongue • Throat: itching, tightness, closure, hoarseness • Skin: itching, hives, eczema, swelling, flushing • Gut: vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain • Lung: shortness of breath, cough, wheeze • Heart: hypotension, dizziness, syncope, tachycardia • Neuro (or head): lightheadedness • Other: feeling of impending doom, anxiety |
Medications prescribed and when they should be used • Epinephrine auto-injectors (first-line); should include detailed instructions (with photographs, if possible) on how to correctly administer the auto-injector device (for daycare, school and/or office staff) • Antihistamines (for cutaneous symptoms) • Inhaled beta2-agonists (for bronchospasm) |
Where medication is stored at home, work or school |
For further reference log on to
https://doi.org/10.1186/s13223-018-0283-4

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd