- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
AIIMS doctors report rare case of cervical congenital infantile fibrosarcoma
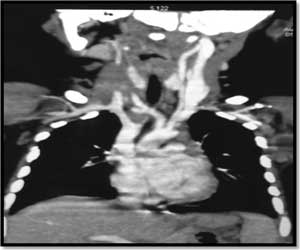
Dr Alisha Gupta at Department of Pediatric Surgery, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India and colleagues have reported a rare case of Congenital infantile fibrosarcoma (CIFS). The case has appeared in the Journal of Medical Case Reports.
Congenital infantile fibrosarcoma (CIFS) is a rare mesenchymal tumour which, contrary to its name, is seen both in children as well as adults. The congenital variety is even rarer with only a few reported cases. Among the sites of origin of these congenital lesions, occurrence in the neck has been reported only once before. The case reported earlier had died during surgery due to exsanguinating haemorrhage. We report here a successful excision of the lesion. The case is discussed with a review of recent literature.
A 3-month-old Hindu baby boy presented with a congenital neck swelling on the right side of his neck. There was no history of birth trauma or breech delivery. Initially a small midline swelling, it progressively increased in size with age. It was soft and compressible with an overlying bluish hue at places. With a working diagnosis of a low flow lymphovascular malformation at another hospital, intralesional bleomycin was injected once after which the swelling became a little firm without any change in its size. One month after the bleomycin injection, it was a 5.5 × 7.5 cm firm, non-tender, well-defined swelling in the midline and extending into the right supraclavicular region.
There was no retrosternal extension and no movement with deglutition or cervical lymphadenopathy. Imaging suggested a diagnosis of lympho-venous malformation. However, there was a remote suspicion of malignancy as there were interspersed solid areas. Serum alpha-fetoprotein levels were in the normal range for age. On exploration, a friable, solid mass with a pseudocapsule was encountered without any cystic component. It encased the sternal head of right sternocleidomastoid, part of which had to be sacrificed. A frozen section sent during excision was suggestive of malignancy. Complete gross resection of the lesion was done. There were no obviously enlarged neck nodes. Histopathology revealed a tumor comprising spindle-shaped fibroblast-like cells along with large areas of hemorrhage.
Tumor cells were arranged in fascicles and at places in a herringbone pattern. There was brisk mitotic activity and moderate degree of anisonucleosis. Cells were immunopositive for desmin but negative for myogenin, smooth muscle actin (SMA), pancytokeratin, epithelial membrane antigen (EMA), MIC-2, and CD-34. The sternocleidomastoid muscle was free of tumor. The diagnosis of CIFS was favored over spindle cell rhabdomyosarcoma in view of absence of myogenin positivity. A metastatic workup was negative. No chemoradiotherapy was initiated and the child was kept under close follow-up. A follow-up contrast-enhanced computed tomography scan (CECT) of his neck and chest showed no residue or recurrence at 3 and 6 months. He is thriving well and was disease free at 2-year follow-up.
A successful excision of cervical congenital infantile fibrosarcoma has not been reported. This diagnosis should be kept as a possibility in all congenital cervical swellings. These are commonly misdiagnosed as lympho-venous malformations and histopathology is confirmatory.
For more details click on the link: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-019-1968-0

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd