- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
ACR and NPF release Joint guideline for psoriatic arthritis
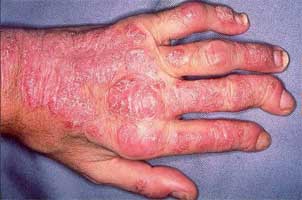
The National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) and the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) have jointly released a treatment guideline for psoriatic arthritis (PsA). This is an evidence-based guideline for the pharmacologic and non-pharmacologic treatment of PsA patients. It also includes recommendations for psoriatic spondylitis, predominant enthesitis, vaccinations, and treatment in the presence of diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease or serious infections.
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a chronic inflammatory musculoskeletal disease commonly found in psoriasis patients. Psoriasis is a skin disease that appearance of red, scaly patches on the skin.
This PsA guideline was developed using the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) methodology, which provides rigorous standards for judging the quality of the literature available and assigns strengths to the recommendations that are largely based on the quality of the available evidence. The quality of evidence was often graded low or very low due to limited data in some areas. This led to nearly all recommendations being conditional.
Key Recommendations:
- A conditional recommendation to use tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi) biologics as a first-line therapy option in patients with active PsA;
- A conditional recommendation to use a treat-to-target approach for all patients with active PsA; and
- A strong recommendation for smoking avoidance/cessation.
"Treat-to-target is key because it encompasses all clinical scenarios, rather than one particular clinical situation," said Jasvinder Singh, a rheumatologist at the University of Alabama at Birmingham who served as principal investigator for the guideline project. "The available evidence suggests the irreversible joint damage, associated functional limitations, joint deformities and disability associated with PsA could possibly be avoided/delayed with optimal disease management using a targeted approach. A targeted approach can also improve pain, function, and quality of life and social participation."
The use of TNFi biologics as a first-line therapy was one of many recommendations included to help providers and patients decide between the various pharmacologic options currently available. While current GRAPPA recommendations address the use of TNFi biologics in treatment-naïve patients, this is the first guideline that specifically recommends first trying them over oral small molecule (OSM) drugs.
"The available evidence suggested that in the absence of certain conditions, many treatment-naïve patients would benefit from trying a TNFi biologic first," said Dafna Gladman, MD, a rheumatology professor of medicine at the University of Toronto and member of the NPF Medical Board who served as a content expert on the guideline's core team. "This doesn't hold true once other symptoms and comorbidities are present, so OSMs can continue to be a first-line option for patients that have contraindications to TNFi treatment, as well as patients without severe PsA or psoriasis that prefer oral therapy. Providers should take into consideration all active disease domains, comorbidities, and the patient's functional status when choosing the optimal therapy for an individual at a given point in time."
Tofacitinib was not included within the OSM category since its benefit/risk profile differs from that of the rest of the OSMs.
The strong recommendation for smoking cessation was based on evidence linking smoking to a reduced efficacy of biologics; the benefits of smoking cessation; and the well-established link of smoking with mortality, cancers and heart and lung diseases in the general population.
"Despite an expansion in the number of new therapies for the treatment of PsA, only limited studies comparing effectiveness exist to inform treatment decisions," said Singh. "This indicates a need for head-to-head trials of various treatments and comparative effectiveness studies in both trial populations and PsA populations with comorbidities. We also need studies in patients with active PsA who are treatment-naïve, or who have tried and failed different treatment approaches. The presence of high-quality evidence will allow the formulation of strong treatment recommendations."
For further reference follow the link: https://doi.org/10.1002/art.40726

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd