- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
2018 NICE Guideline for antibiotic prescription for Acute Sore Throat
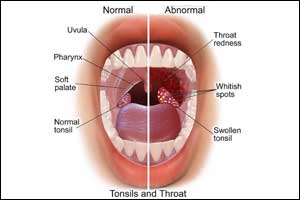
In order to limit the antibiotic use and reduce antimicrobial resistance, National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) has published 2018 guideline on antimicrobial prescribing strategy for an acute sore throat. An acute sore throat which is usually caused by a virus lasts for a week and patients get better without antibiotics. Most of the times non-prescription of antibiotics does not lead to complications.
The Guidance recommends that the treating Doctors patients should note that -
- Acute sore throat (including pharyngitis and tonsillitis) is self‑limiting and often triggered by a viral infection of the upper respiratory tract
- symptoms can last for around 1 week, but most people will get better within this time without antibiotics, regardless of cause (bacteria or virus).
- Assess and manage children under 5 who present with fever as outlined in the NICE guideline on fever in under 5s. Clinicians should not use a response to antipyretic therapy alone as a means to differentiate between serious and non-serious infection
- Use FeverPAIN or Centor criteria to identify people who are more likely to benefit from an antibiotic.Each of the FeverPAIN criteria score 1 point (maximum score of 5). Higher scores suggest more severe symptoms and likely bacterial (streptococcal) cause. A score of 0 or 1 is thought to be associated with a 13 to 18% likelihood of isolating streptococcus. A score of 2 or 3 is thought to be associated with a 34 to 40% likelihood of isolating streptococcus. A score of 4 or 5 is thought to be associated with a 62 to 65% likelihood of isolating streptococcus.Centor criteria include
• Tonsillar exudate
• Tender anterior cervical lymphadenopathy or lymphadenitis
• History of fever (over 38°C)
• Absence of cough - Give advice about:
- the usual course of acute sore throat (can last around 1 week)
- managing symptoms, including pain, fever and dehydration, with self-care (see the recommendations on self-care).
4.Reassess at any time if symptoms worsen rapidly or significantly, taking account of:
- alternative diagnoses such as scarlet fever or glandular fever
- any symptoms or signs suggesting a more serious illness or condition
- previous antibiotic use, which may lead to resistant organisms.
In people who are unlikely to benefit from an antibiotic (Fever PAIN score of 0 or 1, or Centor score of 0, 1 or 2):
- Do not offer an antibiotic prescription.
- Guide them to seek medical help if symptoms worsen rapidly or significantly, do not start to improve after 1 week, or the person becomes systemically very unwell
Recommendations about Choice of antibiotic
When prescribing an antibiotic for acute sore throat:
- follow table 1 for adults aged 18 years and over.
- follow table 2 for children and young people under 18 years.
Table 1 Antibiotics for adults aged 18 years and over
| Antibiotic 1 | Dosage and course length for adults 2 |
| First choice | |
| Phenoxymethylpenicillin | 500 mg four times a day or 1,000 mg twice a day for 5 to 10 days |
| Alternative first choices for penicillin allergy or intolerance 3 | |
| Clarithromycin | 250 mg to 500 mg twice a day for 5 days |
| Erythromycin | 250 mg to 500 mg four times a day or 500 mg to 1,000 mg twice a day for 5 days |
| 1See BNF for appropriate use and dosing in specific populations, for example, hepatic impairment, renal impairment, pregnancy and breastfeeding. 2Doses given are by mouth using immediate-release medicines, unless otherwise stated. 3Erythromycin is preferred in women who are pregnant. | |
Table 2 Antibiotics for children and young people under 18 years
| Antibiotic 1 | Dosage and course length for children and young people 2 |
| First choice | |
| Phenoxymethylpenicillin | 1 to 11 months, 62.5 mg four times a day or 125 mg twice a day for 5 to 10 days 1 to 5 years, 125 mg four times a day or 250 mg twice a day for 5 to 10 days 6 to 11 years, 250 mg four times a day or 500 mg twice a day for 5 to 10 days 12 to 17 years, 500 mg four times a day or 1,000 mg twice a day for 5 to 10 days |
| Alternative first choices for penicillin allergy or intolerance 3 | |
| Clarithromycin | 1 month to 11 years: Under 8 kg, 7.5 mg/kg twice a day for 5 days 8 to 11 kg, 62.5 mg twice a day for 5 days 12 to 19 kg, 125 mg twice a day for 5 days 20 to 29 kg, 187.5 mg twice a day for 5 days 30 to 40 kg, 250 mg twice a day for 5 daysor 12 to 17 years, 250 mg to 500 mg twice a day for 5 days |
| Erythromycin | 1 month to 1 year, 125 mg four times a day or 250 mg twice a day for 5 days 2 to 7 years, 250 mg four times a day or 500 mg twice a day for 5 days 8 to 17 years, 250 mg to 500 mg four times a day or 500 mg to 1,000 mg twice a day for 5 days |
| 1See BNF for children for appropriate use and dosing in specific populations, for example hepatic impairment and renal impairment. 2The age bands apply to children of average size and, in practice, the prescriber will use the age bands in conjunction with other factors such as the severity of the condition and the child's size in relation to the average size of children of the same age. Doses given are by mouth using immediate‑release medicines, unless otherwise stated. 3Erythromycin is preferred in young women who are pregnant. | |
For further reference log on to :
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng84
For visual summary log on to :
breastfeedingClarithromycinErythromycinNational Institute for Health and Care ExcellenceNICE guidelinesPhenoxymethylpenicillin
Next Story
NO DATA FOUND

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd