- Home
- Editorial
- News
- Practice Guidelines
- Anesthesiology Guidelines
- Cancer Guidelines
- Cardiac Sciences Guidelines
- Critical Care Guidelines
- Dentistry Guidelines
- Dermatology Guidelines
- Diabetes and Endo Guidelines
- Diagnostics Guidelines
- ENT Guidelines
- Featured Practice Guidelines
- Gastroenterology Guidelines
- Geriatrics Guidelines
- Medicine Guidelines
- Nephrology Guidelines
- Neurosciences Guidelines
- Obs and Gynae Guidelines
- Ophthalmology Guidelines
- Orthopaedics Guidelines
- Paediatrics Guidelines
- Psychiatry Guidelines
- Pulmonology Guidelines
- Radiology Guidelines
- Surgery Guidelines
- Urology Guidelines
1 in 10 young patients with MI will have familial hypercholesterolemia: JACC Study
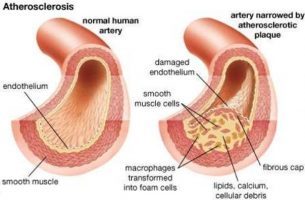
USA: Clinically defined familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is prevalent in nearly 10% of young adults with myocardial infarction (MI), according to a recent study. Only two-thirds of FH patients were discharged on high-intensity statin therapy, and the vast majority had elevated LDL-C at 1 year.
The findings, published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, reinforce the need for more aggressive lipid-lowering therapy in young FH and non-FH patients post-MI.
Familial hypercholesterolemia is a common autosomal dominant disease caused by a defect on chromosome 19. This makes the removal of low-density lipoprotein (LDL, or bad) cholesterol from the blood difficult leading to an increased level of serum LDL cholesterol. FH increases the risk of coronary heart disease.
There are limited data on the prevalence and treatment of familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) among U.S. adults who experience a myocardial infarction at a young age. Avinainder Singh, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, MA, and colleagues conducted this retrospective cohort study to evaluate the prevalence of clinically defined FH and examine the rates of statin utilization and LDL-C achieved 1-year post-MI.
The YOUNG-MI registry included 1,996 adults with a median age of 45 years patients (19% were women, and 54% had ST-segment elevation MI) who experienced an MI at or below age 50 years between 2000 and 2016. Probable or definite FH was defined by the Dutch Lipid Clinic criteria. Outcomes included the proportion of patients classified as probable or definite FH, use of lipid-lowering therapy, and LDL-C achieved 1-year post MI.
Also Read: Familial hypercholesterolemia does not increase risk of heart attack, finds study
Key Findings:
- Probable/definite FH was present in 180 (9%) of whom 42.8% were not on statins prior to their MI.
- Of the 1,966 patients surviving until hospital discharge, 89.4% of FH patients and 89.9% of non-FH patients were discharged on statin therapy.
- Among FH patients, 63.3% were discharged on high-intensity statin compared with 48.4% for non-FH patients.
- At 1-year follow-up, the percent reduction in LDL-C among FH patients was −44.4% compared with −34.5% in non-FH patients.
- The proportion of patients with LDL-C ≥70 mg/dl was higher among FH patients (82.2%) compared with non-FH patients (64.5%).
Also Read: Medical Treatment of Familial Hypercholesterolemia
"There was no difference in all-cause mortality in long-term follow-up between the FH and non-FH patients, adding that for this reason, it’s hard to justify add-on lipid-lowering therapy, such as ezetimibe or the PCSK9 inhibitors," editorialists write in an accompanying editorial. They, however, caution against drawing firm conclusions because the study was underpowered for fatal events in this relatively young patient population.
For detailed study log on to DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.02.059

Disclaimer: This site is primarily intended for healthcare professionals. Any content/information on this website does not replace the advice of medical and/or health professionals and should not be construed as medical/diagnostic advice/endorsement or prescription. Use of this site is subject to our terms of use, privacy policy, advertisement policy. © 2020 Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt Ltd